Binary Representation Of Numbers Worksheet - Autar Kaw, University Of South Florida
ADVERTISEMENT
Binary Representation of Numbers
Autar Kaw
After reading this chapter, you should be able to:
1. convert a base-10 real number to its binary representation,
2. convert a binary number to an equivalent base-10 number.
In everyday life, we use a number system with a base of 10. For example, look
at the number 257.56. Each digit in 257.56 has a value of 0 through 9 and has a place
value. It can be written as
2
1
0
−
1
−
2
257
.
76
=
2
×
10
+
5
×
10
+
7
×
10
+
7
×
10
+
6
×
10
In a binary system, we have a similar system where the base is made of only two digits
0 and 1. So it is a base 2 system. A number like (1011.0011) in base-2 represents the
decimal number as
(
)
3
2
1
0
−
1
−
2
−
3
−
4
(
1011
.
0011
)
=
1 (
×
2
+
0
×
2
+
1
×
2
+
1
×
2
)
+
0 (
×
2
+
0
×
2
+
1
×
2
+
1
×
2
)
2
10
=
11
.
1875
in the decimal system.
To understand the binary system, we need to be able to convert binary numbers
to decimal numbers and vice-versa.
We have already seen an example of how binary numbers are converted to
decimal numbers. Let us see how we can convert a decimal number to a binary
number. For example take the decimal number 11.1875. First, look at the integer part:
11.
1. Divide 11 by 2. This gives a quotient of 5 and a remainder of 1. Since the
remainder is 1,
.
a
=
1
0
2. Divide the quotient 5 by 2. This gives a quotient of 2 and a remainder of 1.
Since the remainder is 1,
.
a
=
1
1
3. Divide the quotient 2 by 2. This gives a quotient of 1 and a remainder of 0.
Since the remainder is 0,
.
a
=
0
2
4. Divide the quotient 1 by 2. This gives a quotient of 0 and a remainder of 1.
Since the remainder is ,
.
a
=
1
3
Source URL:
Saylor URL:
Attributed to: University of South Florida: Holistic Numerical Methods Institute
Page 1 of 12
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3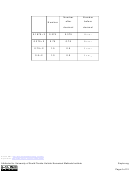 4
4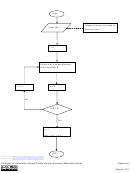 5
5 6
6 7
7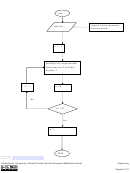 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12








