Chapter 11 Three Dimensional Geometry Worksheet Page 11
ADVERTISEMENT
THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
473
H
H
+
+
+
+
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
Solution
Here
=
and
=
b
i
2
j
2
k
b
3
i
2
j
6
k
1
2
The angle θ between the two lines is given by
H H
⋅
+
+
⋅
+
+
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
b b
(
i
2
j
2 ) (3
k
i
2
j
6 )
k
=
cos θ =
H H
1
2
+ +
+ +
1 4 4 9 4 36
b b
1
2
+ +
3 4 12
19
=
=
×
3 7
21
19
θ = cos
–1
Hence
21
Example 10
Find the angle between the pair of lines
x +
−
+
3
y
1
z
3
=
=
3
5
4
x +
−
−
1
y
4
z
5
=
and
=
1
1
2
Solution
The direction ratios of the first line are 3, 5, 4 and the direction ratios of the
second line are 1, 1, 2. If θ is the angle between them, then
+
+
3.1 5.1 4.2
16
16
8 3
=
=
=
cos θ =
+
+
+
+
15
2
2
2
2
2
2
50 6
5 2 6
3
5
4
1
1
2
8 3
–1
Hence, the required angle is cos
.
15
11.5 Shortest Distance between Two Lines
If two lines in space intersect at a point, then the shortest distance between them is
zero. Also, if two lines in space are parallel,
then the shortest distance between them
will be the perpendicular distance, i.e. the
length of the perpendicular drawn from a
point on one line onto the other line.
Further, in a space, there are lines which
are neither intersecting nor parallel. In fact,
such pair of lines are non coplanar and
are called skew lines. For example, let us
consider a room of size 1, 3, 2 units along
Fig 11.7
x, y and z-axes respectively Fig 11.7.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21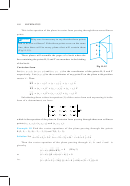 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27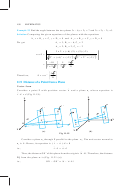 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41








