Math 251 Worksheet With Answers
ADVERTISEMENT
Math 251
Notes
Solutions
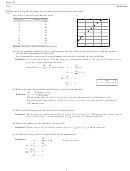
6. The age of a dog and its relative age in human years is shown in the table below.
Dog Years Compared with Human Years
h
80
Dog Years
Human Years
1
16
70
2
24
60
3
28
50
5
36
40
7
44
9
52
30
11
60
20
13
68
10
15
76
d
0
Source: American Animal Hospital Association
0
5
10
15
20
Dog Years
(a) Use your graphing calculator to plot a scattergram of the data. Then use the space below to find the equation
of a line that approximates the data well.
Let h represent the relative age of a dog in human years and let d represent the dog’s actual age.
Solution: (see scatter plot above.) The line that goes through the points (1, 16) and (15, 76) seems to do a
good job of approximating the data.
60
30
30
From these m =
=
and we have
h =
d + b
14
7
7
30
16 =
(1) + b
7
30
16
= b
7
30
5
5
h =
d + 11
11
= b
7
7
7
(b) What is the slope of your model and what does it mean in this situation?
30
30 human years
Solution:
7
7 dog years
Which means that for every 7 dog years a dog ages the equivalent of 30 human years.
For the decimal equivalent, m
4.29 or for every one dog year a dog ages the equivalent of
4.29 human years.
(c) What is the h-intercept and what does it mean in this situation?
5
Solution: The h-intercept (which occurs when d = 0) is 11
or about 11.7. This means that when a dog is
7
5
born (0 dog years), it is the equivalent of 11
or about 11.7 human years old.
7
(d) What is the relative age of a dog that is 18 years old?
30
5
Solution: When a dog is 18, its relative human age is h =
(18) + 11
88.86 years old.
7
7
(e) At what age (in dog years) is a dog’s relative age 40 human years?
30
5
Solution:
40 =
d + 11
So 6.6 dog years.
7
7
5
30
40
11
=
d
7
7
7
198
= d
30
7
6.6 = d
1
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2