Vsepr Chart Worksheet
ADVERTISEMENT
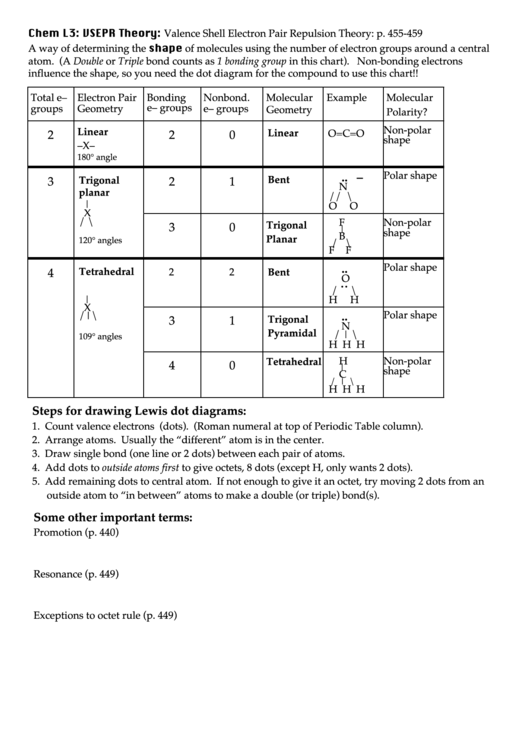
Chem L3: VSEPR Theory: Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory: p. 455-459
A way of determining the shape of molecules using the number of electron groups around a central
atom. (A Double or Triple bond counts as 1 bonding group in this chart). Non-bonding electrons
influence the shape, so you need the dot diagram for the compound to use this chart!!
Total e–
Electron Pair
Bonding
Nonbond.
Molecular
Example
Molecular
e– groups
groups
Geometry
e– groups
Geometry
Polarity?
Non-polar
Linear
2
2
0
Linear
O=C=O
shape
–X–
180° angle
Polar shape
.. –
Trigonal
Trigonal
Bent
3
3
2
1
N
planar
planar
// \
|
|
O
O
X
X
/ \
/ \
F
Non-polar
Trigonal
3
0
|
shape
B
Planar
120° angles
120° angles
/ \
F ! F
Polar shape
..
4
4
4
Tetrahedral
Tetrahedral
Tetrahedral
2
2
Bent
O
˙˙
/
\
|
|
|
H
H
X
X
X
Polar shape
..
/|\
/|\
/|\
3
1
Trigonal
N
Pyramidal
/ | \
109° angles
109° angles
109° angles
H H H
H
Non-polar
Tetrahedral
4
0
|
shape
C
/ | \
H H H
Steps for drawing Lewis dot diagrams:
1. Count valence electrons (dots). (Roman numeral at top of Periodic Table column).
2. Arrange atoms. Usually the “different” atom is in the center.
3. Draw single bond (one line or 2 dots) between each pair of atoms.
4. Add dots to outside atoms first to give octets, 8 dots (except H, only wants 2 dots).
5. Add remaining dots to central atom. If not enough to give it an octet, try moving 2 dots from an
outside atom to “in between” atoms to make a double (or triple) bond(s).
Some other important terms:
Promotion (p. 440)
Resonance (p. 449)
Exceptions to octet rule (p. 449)
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2