Naming Chemical Compounds
ADVERTISEMENT
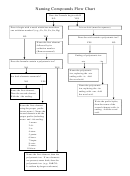
Naming Chemical Compounds
Chemical compounds can be divided into two basic types,
ionic
and covalent.
Ionic compounds are easily recognized because they contain a metal and a
nonmetal. Covalent compounds are those which contain only nonmetals. The
periodic table in the front cover of your text shows which elements fall into each
class.
The names for ionic compounds are very simple. The first part of the name is
simply the name of the metal element. The second part of the name is the name
of the nonmetal element, with the ending changed to the suffix –ide.
For
example, consider the compound
Al
O
. While the subscripts indicate that the
2
3
compound consists of two atoms of aluminum and three atoms of oxygen, these
numbers do not affect the name. The first part of the name would be aluminum.
For the second part of the name, we drop the ending on oxygen and add –ide,
thus it becomes oxide. The name of the compound is then
aluminum
oxide.
When an ionic compound contains a transition metal, the names become a bit
more complicated.
The metals in the d and f blocks can have more than one
charge and can thus form more than one compound. For example, iron and
chlorine form two different compounds,
FeCl
and
FeCl
.
To distinguish them,
2
3
we add a Roman numeral to indicate the charge on the metal ion. For FeCl
, the
2
total charge on the two chloride ions is 2-, thus the iron must have a charge of 2+
to balance. The name of this compound is then
iron(II)
chloride. For FeCl
, the
3
total charge on three chloride ions is 3-, so the iron will have a charge of 3+ and
the name of the compound is
iron(III)
chloride.
There is a special class of ions known as
polyatomic
ions. These ions consist of two
or more nonmetal atoms
covalently
bonded together, and the entire group has a
positive or negative charge. You will be responsible for learning a total of eight of
these ions, but by applying some simple rules, you can determine the formulas and
names of many more. These three rules are
1.
Add a hydrogen atom to a polyatomic anion. This reduces the negative
charge on the ion by one and the word hydrogen is added to the beginning
-
2
of the name. For example, the
carbonate ion
has the formula
CO
. A
3
hydrogen can be added to the ion to form the
hydrogen carbonate
ion,
-
which has a formula of
HCO
.
3
2.
An oxygen can be removed from an ion. This does not affect the charge
and the ending of the name is changed from
–ate
to –ite. The
nitrate ion
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4