Electrical Conductivity Of Aqueous Solutions
ADVERTISEMENT
Electrical Conductivity of Aqueous Solutions
Objectives
The objectives of this laboratory are:
a) To observe electrical conductivity of substances in various aqueous solutions
b) To determine of the solution is a strong or weak electrolyte
c) To interpret a chemical reaction by observing aqueous solution conductivity.
Background
Electrical conductivity is based on the flow of electrons.
Metals are good conductors of
electricity because they allow electrons to flow through the entire piece of material. Thus,
electrons flow like a “sea of electrons” through metals. In comparison, distilled water is a very
poor conductor of electricity since very little electricity flows through water. Highly ionized
substances are strong electrolytes. Strong acids and salts are strong electrolytes because they
completely ionize (dissociate or separate) in solution. The ions carry the electric charge through
the solution thus creating an electric current. The current, if sufficient enough, will light one or
both LEDs on a conductivity meter, shown at right.
Slightly ionized substances are weak electrolytes. Weak acids and bases would be categorized
as weak electrolytes because they do not completely dissociate in solution.
Substances that do not conduct an electric current are called non-electrolytes. Non-electrolytes
do not ionize; they do not contain moveable ions. The LEDs of a conductivity meter will not
light because there are no ions to carry the electric current. The table below lists examples of
strong, weak and non-electrolytes.
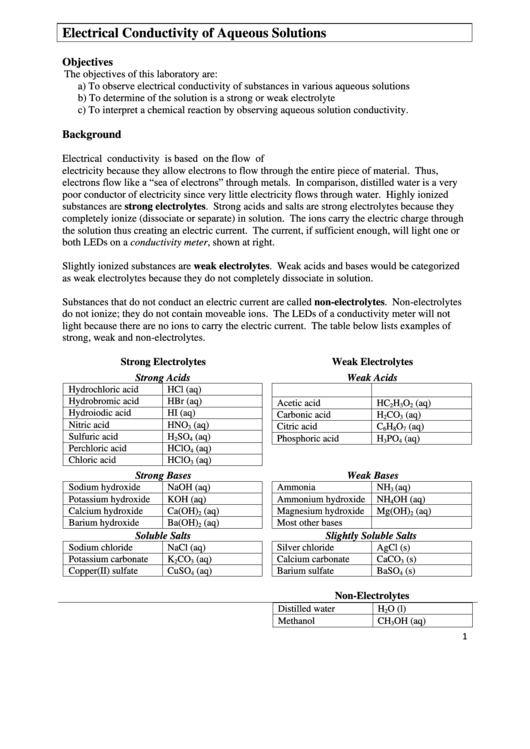
Strong Electrolytes
Weak Electrolytes
Strong Acids
Weak Acids
Hydrochloric acid
HCl (aq)
Hydrobromic acid
HBr (aq)
Acetic acid
HC
H
O
(aq)
2
3
2
Hydroiodic acid
HI (aq)
Carbonic acid
H
CO
(aq)
2
3
Nitric acid
HNO
(aq)
Citric acid
C
H
O
(aq)
3
6
8
7
Sulfuric acid
H
SO
(aq)
Phosphoric acid
H
PO
(aq)
2
4
3
4
Perchloric acid
HClO
(aq)
4
Chloric acid
HClO
(aq)
3
Strong Bases
Weak Bases
Sodium hydroxide
NaOH (aq)
Ammonia
NH
(aq)
3
Potassium hydroxide
KOH (aq)
Ammonium hydroxide
NH
OH (aq)
4
Calcium hydroxide
Ca(OH)
(aq)
Magnesium hydroxide
Mg(OH)
(aq)
2
2
Barium hydroxide
Ba(OH)
(aq)
Most other bases
2
Soluble Salts
Slightly Soluble Salts
Sodium chloride
NaCl (aq)
Silver chloride
AgCl (s)
Potassium carbonate
K
CO
(aq)
Calcium carbonate
CaCO
(s)
2
3
3
Copper(II) sulfate
CuSO
(aq)
Barium sulfate
BaSO
(s)
4
4
Non-Electrolytes
Distilled water
H
O (l)
2
Methanol
CH
OH (aq)
3
1
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Business
 1
1 2
2 3
3








