Bond Enthalpies
ADVERTISEMENT
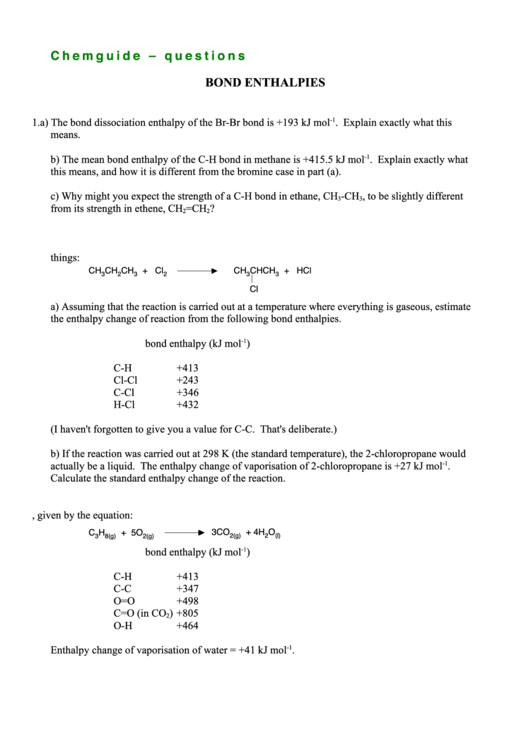
C h e m g u i d e – q u e s t i o n s
BOND ENTHALPIES
1. a) The bond dissociation enthalpy of the Br-Br bond is +193 kJ mol
-1
. Explain exactly what this
means.
b) The mean bond enthalpy of the C-H bond in methane is +415.5 kJ mol
-1
. Explain exactly what
this means, and how it is different from the bromine case in part (a).
c) Why might you expect the strength of a C-H bond in ethane, CH
-CH
, to be slightly different
3
3
from its strength in ethene, CH
=CH
?
2
2
2. Propane and chlorine react in the presence of UV light to give 2-chloropropane amongst other
things:
CH
CH
CH
+ Cl
CH
CHCH
+ HCl
3
2
3
2
3
3
Cl
a) Assuming that the reaction is carried out at a temperature where everything is gaseous, estimate
the enthalpy change of reaction from the following bond enthalpies.
bond enthalpy (kJ mol
-1
)
C-H
+413
Cl-Cl
+243
C-Cl
+346
H-Cl
+432
(I haven't forgotten to give you a value for C-C. That's deliberate.)
b) If the reaction was carried out at 298 K (the standard temperature), the 2-chloropropane would
actually be a liquid. The enthalpy change of vaporisation of 2-chloropropane is +27 kJ mol
-1
.
Calculate the standard enthalpy change of the reaction.
3. Calculate the standard enthalpy change of combustion of propane, given by the equation:
3CO
+ 4H
O
C
H
+ 5O
2(g)
2
(l)
3
8(g)
2(g)
-1
bond enthalpy (kJ mol
)
C-H
+413
C-C
+347
O=O
+498
C=O (in CO
) +805
2
O-H
+464
Enthalpy change of vaporisation of water = +41 kJ mol
-1
.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1








