Introduction To Energy Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
Introduction to Energy
What is Energy?
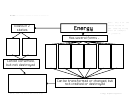
ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS
Energy makes change; it does things for us. It moves cars along the
road and boats over the water. It bakes a cake in the oven and keeps
POTENTIAL
ice frozen in the freezer. It plays our favorite songs on the radio and
lights our homes. Energy makes our bodies grow and allows our
Stored energy and the energy of position (gravitational).
minds to think. Scientists define energy as the ability to do work.
Forms of Energy
CHEMICAL ENERGY is the energy stored in the bonds of atoms and
molecules. Biomass, petroleum, natural gas, propane and coal are
Energy is found in different forms, such as light, heat, sound, and
examples.
motion. There are many forms of energy, but they can all be put into
two categories: kinetic and potential.
NUCLEAR ENERGY is the energy stored in the nucleus of an atom – the
energy that holds the nucleus together. The nucleus of a uranium atom
Kinetic Energy
is an example.
STORED MECHANICAL ENERGY is energy stored in objects by the
Kinetic energy is motion; it is the motion of waves, electrons, atoms,
application of force. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands
molecules, substances, and objects.
are examples.
Electrical Energy
is the movement of electrons. Everything is made
GRAVITATIONAL ENERGY is the energy of place or position. Water in a
of tiny particles called atoms. Atoms are made of even smaller
reservoir behind a hydropower dam is an example.
particles called electrons, protons, and neutrons. Applying a force
can make some of the electrons move. Electrons moving through
a wire is called circuit electricity. Lightning is another example of
KINETIC
electrical energy.
Motion: the motion of waves, electrons, atoms,
Radiant Energy
is electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse
molecules and substances.
waves. Radiant energy includes visible light, x-rays, gamma rays, and
radio waves. Light is one type of radiant energy. Solar energy is an
example of radiant energy.
RADIANT ENERGY is electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse
Thermal Energy,
or heat, is the internal energy in substances; it is
waves. Solar energy is an example.
the vibration and movement of the atoms and molecules within
THERMAL ENERGY or heat is the internal energy in substances – the
substances. The more thermal energy in a substance, the faster the
vibration or movement of atoms and molecules in substances. Geo-
atoms and molecules vibrate and move. Geothermal energy is an
thermal is an example.
example of thermal energy.
MOTION is the movement of a substance from one placed to another.
Sound
is the movement of energy through substances in longitudinal
Wind and hydropower are examples.
(compression/rarefaction) waves. Sound is produced when a force
SOUND is the movement of energy through substances in longitudinal
causes an object or substance to vibrate; the energy is transferred
waves.
through the substance in a longitudinal wave.
ELECTRICAL ENERGY is the movement of electrons. Lightning and
Motion
is the movement of objects and substances from one place
electricity are examples.
to another. Objects and substances move when a force is applied
according to Newton’s Laws of Motion. Wind is an example of motion
energy.
Potential Energy
Chemical
Motion
Chemical
Motion
Potential energy is stored energy and the energy of position, or
gravitational energy. There are several forms of potential energy.
Chemical Energy
is energy stored in the bonds of atoms and
molecules. It is the energy that holds these particles together.
Radiant
Chemical
Electrical
Thermal
Biomass, petroleum, natural gas, and propane are examples of
stored chemical energy.
6
Intermediate Energy Infobook
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4








