Math Cheat Sheet
ADVERTISEMENT
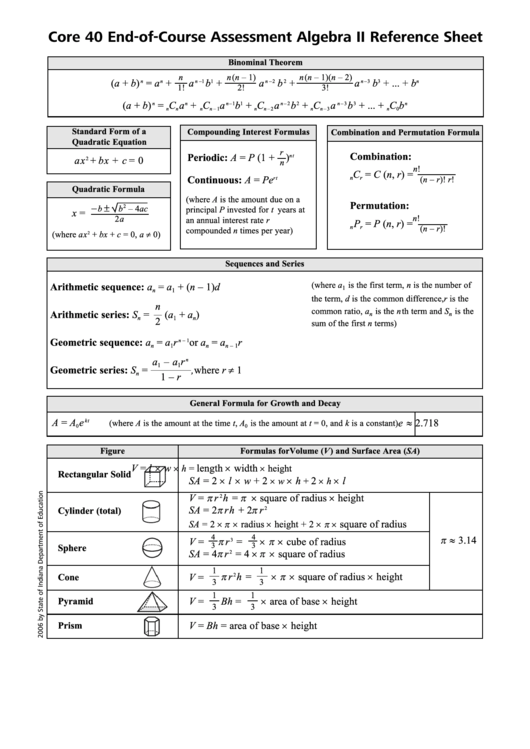
Core 40 End-of-Course Assessment Algebra II Reference Sheet
Binominal Theorem
n
n(n – 1)
n (n – 1)(n – 2)
(a + b)
n
= a
n
+
a
n –1
b
1
+
a
n – 2
b
2
+
a
n – 3
b
3
+ ... + b
n
1!
2!
3!
(a + b)
n
=
C
a
n
+
C
a
n –1
b
1
+
C
a
n – 2
b
2
+
C
a
n – 3
b
3
+ ... +
C
b
n
n
n
n
n –1
n
n – 2
n
n – 3
n
0
Standard Form of a
Compounding Interest Formulas
Combination and Permutation Formula
Quadratic Equation
r
Combination:
Periodic: A = P (1 +
)
n t
ax
2
+ bx + c = 0
n
n!
C
= C (n, r) =
n
r
Continuous: A = Pe
r t
(n – r)! r!
Quadratic Formula
(where A is the amount due on a
±
Permutation:
–
2
b
b
– 4ac
principal P invested for t years at
x =
n!
2a
an annual interest rate r
P
= P (n, r) =
n
r
(n – r)!
compounded n times per year)
+ bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0)
(where ax
2
Sequences and Series
(where a
is the first term, n is the number of
Arithmetic sequence: a
= a
+ (n – 1) d
1
n
1
the term, d is the common difference, r is the
n
common ratio, a
is the nth term and S
is the
___
Arithmetic series: S
=
(a
+ a
)
n
n
n
1
n
2
sum of the first n terms)
Geometric sequence: a
= a
r
n – 1
or a
= a
r
n
1
n
n – 1
a
– a
r
n
1
1
,where r ≠ 1
_______________
Geometric series: S
=
n
1 – r
General Formula for Growth and Decay
e ≈ 2.718
A = A
e
kt
(where A is the amount at the time t, A
is the amount at t = 0, and k is a constant)
0
0
Figure
Formulas for Volume (V) and Surface Area (SA)
V = l × w
length × width
× h =
× height
Rectangular Solid
SA = 2 × l × w + 2
× h
× l
× w
× h
2
+
V = π r
h = π × square of radius × height
2
SA = 2 π rh + 2 π r
2
Cylinder (total)
SA = 2 × π × radius × height + 2 × π ×
square of radius
π ≈ 3.14
4
4
π r
× π × cube of radius
V =
3
=
3
3
Sphere
SA = 4 π r
= 4 × π × square of radius
2
1
1
π r
× π × square of radius × height
V =
2
h =
Cone
3
3
1
1
× area of base × height
V =
Bh =
Pyramid
3
3
V = Bh = area of base × height
Prism
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2