Spectroscopic Tables Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
APPENDICES
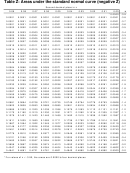
INFRA-RED GROUP ABSORPTION FREQUENCIES
FREQUENCY (cm -1 )
TYPE OF VIBRATION
WAVELENGTH (µ)
INTENSITY (1)
CH
Alkanes
(stretch)
3000-2850
3.33-3.51
s
CH 3
(bend)
1450 and 1375
6.90 and 7.27
m
CH 2
(bend)
1465
6.83
m
Alkenes
(stretch)
3100-3000
3.23-3.33
m
(bend)
1700-1000
5.88-10.0
s
Aromatics
(stretch)
3150-3050
3.17-3.28
s
(out-of-plane bend)
1000-700
10.0-14.3
s
Alkyne
(stretch)
ca. 3300
ca.3.03
s
Aldehyde
2900-2800
3.45-3.57
w
2800-2700
3.57-3.70
w
CC
Alkane
not usually useful
C=C
Alkene
1680-1600
5.95-6.25
m-w
Aromatic
1600-1400
6.25-7.14
m-w
CC
Alkyne
2250-2100
4.44-4.76
m-w
C=O
Aldehyde
1740-1720
5.75-5.81
s
Ketone
1725-1705
5.80-5.87
s
Carboxylic acid
1725-1700
5.80-5.88
s
Ester
1750-1730
5.71-5.78
s
Amide
1700-1640
5.88-6.10
s
Anhydride
ca. 1810
ca. 5.52
s
ca. 1760
ca. 5.68
s
Acyl chloride
1800
5.55
s
CO
Alcohols, Ethers, Esters,
Carboxylic acids
1300-1000
7.69-10.0
s
OH
Alcohols, Phenols
Free
3650-3600
2.74-2.78
m
H-Bonded
3400-3200
2.94-3.12
m
Carboxylic acids (2)
3300-2500
3.03-4.00
m
NH
Primary and secondary amines
ca. 3500
ca. 2.86
m
CN
Nitriles
2260-2240
4.42-4.46
m
N=O
Nitro (RNO 2 )
1600-1500
6.25-6.67
s
1400-1300
7.14-7.69
s
CX
Fluoride
1400-1000
7.14-10.0
s
Chloride
800-600
12.5-16.7
s
Bromide, Iodide
<600
>16.7
s
___________________________________________________________________________________
(1) s = strong, m = medium and w = weak
(2) note that the -OH absorption of solid carboxylic acids which run as a nujol mull can be difficult to see as they maybe very broad
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1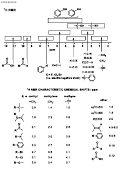 2
2 3
3 4
4