The Causal Analysis Essay Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
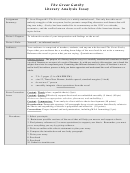
Fulfill one of the three purposes for causal analysis:
a.
To prove a point
b.
To argue against a widely accepted belief
c.
To speculate on a theory
Write a thesis sentence that tells whether the essay focuses on cause, effect, or both.
Use a variety of rhetorical forms to develop the essay - description, narration, example,
classification, or comparison/contrast.
Decide on a logical organizational pattern.
a.
Single cause - multiple effects
b.
Multiple causes - single effect
c.
Causal chain
Develop the general assertions with sufficient specific details.
Coherently link ideas with effective transitions between major ideas and issues of
cause/effect.
Avoid logical fallacies in cause/effect relationships.
- Post hoc, ergo propter hoc (after this, therefore because of this)
- Oversimplification of a situation
- Insufficient evidence and specific details
- Omitting important connections
- Lack of honesty
Effective causal analysis requires that the writer seek more than just the immediate causes or
effects. It demands that the writer use more complex thinking and delve into the more basic
or ultimate causes of effects.
Causal analysis provides a benefit to both the reader and the writer.
a.
It attempts to answer the “why” in our lives.
b.
It provides ways for us to clarify our view of the world we live in.
c.
It allows us to begin to understand the often complex series of events that shape
our lives.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3