Risk Management Plan Page 6
ADVERTISEMENT
Minor (D)
No regulatory action anticipated
No compliance impact anticipated
No evident security threat affected
Minor errors in completed Company policy & procedures
Production errors containing quality system and / or opportunities for improvement
Negligible (E)
No regulatory/compliance violation
No security/confidentiality element affected
On time production
Validated experiments
“Clean” product
Properly executed communications
For each of the impact categories the impact assessment should include consideration of the
following areas of impact also:
• Cost – This impact is usually estimated as a dollar amount that has a direct impact to the
project. However, cost is sometimes estimated and reported as simply additional resources,
equipment, etc. This is true whenever these additional resources will not result in a direct
financial impact to the project due to the fact the resources are loaned or volunteer, the
equipment is currently idle and there is no cost of use, or there are other types of donations that
won’t impact the project budget. Regardless of whether there is a direct cost, the additional
resources should be documented in the risk statement as part of the mitigation cost.
• Scope – Whenever there is the potential that the final product will not be completed as
originally envisioned there is a scope impact. Scope impact could be measured as a reduction of
the number of studies completed, or not providing a deliverable such as an IND.
• Schedule – It is very important to estimate the schedule impact of a risk event as this often
results is the basis for elevating the other impact categories. Schedule delays frequently result in
cost increases and may result in a reduction of scope or quality. Schedule delays may or may not
impact the critical path of the project and an associated push out of the final end date.
• Performance/Quality – Performance/Quality is frequently overlooked as an impact category
and too often a reduction in quality is the preferred choice for mitigation of a risk. “Short cuts”
and “low cost replacements” are ways of reducing cost impacts. If not documented appropriately
and approved by the project sponsor, mitigation strategies that rely upon a reduction in quality
can result in significant disappointment by the stakeholders.
Most risks will be assigned one category, but some might be assigned more than one, or all.
2.4 Risk Response
For each identified risk, a response must be identified. It is the responsibility of the project team
to select a risk response for each risk. The project team will need the best possible assessment of
the risk and description of the response options in order to select the right response for each risk.
The probability of the risk event occurring and the impacts will be the basis for determining the
degree to which the actions to mitigate the risk should be taken. One way of evaluating
mitigation strategies is to multiply the risk cost times the probability of occurrence. Mitigation
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Business
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8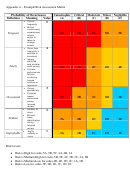 9
9 10
10








