Critical-Path Analysis For Network Scheduling Page 12
ADVERTISEMENT
Highway Example
A three-kilometer highway stretch is divided to ten sections for planning purposes. Each section is 300 meters.
The cross section is shown below along with activities’ details.
1.8 m
10 m
0.9 m
1.5 m
Total excavation thickness:
Middle = 500mm; and
Shoulders = 200 mm.
Activities’ estimates are as follows:
Estimate 1
Estimate 2
Estimate 3
Cost
Time
Cost
Time
Cost
Time
Activity
($)
(days)
($)
(days)
($)
(days)
1. Excavation
21,000
3
30,000
2
----
----
2. Sub-base
7,800
2
----
----
----
----
3. Base
72,000
10
80,000
8
100,000
5
4. Binder
30,000
1.2
----
----
----
----
5. Asphalt
14,400
1
----
----
----
----
6. Curbs
31,200
2
38,000
1
----
----
7. Lighting
19,245
2
25,000
1
----
----
8. Sidewalks
10,950
2
----
----
----
----
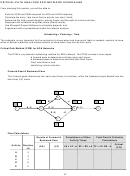
The logical relationships are shown. Also, for all activities,
seasonal productivity factors are: Winter = 0.65; Spring = 1.0;
and Fall = 0.85.
Requirements:
Use the Repetitive Schedule feature of EasyPlan to
-
develop an optimum schedule.
Deadline = 30 days and the project starts June 1, 2006.
-
How will your plan differ if you start the whole project on Feb. 1, 2006?
-
How will your plan differ if you have a maximum of 3 crews for each activity?
-
How will your plan differ if you start the whole project from one side as opposed to employing half the
-
crews from each side?
58
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1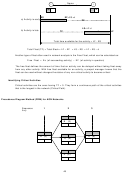 2
2 3
3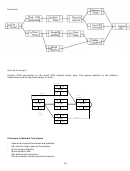 4
4 5
5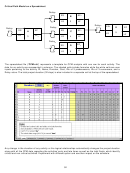 6
6 7
7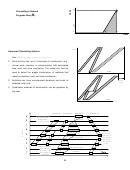 8
8 9
9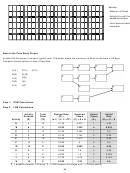 10
10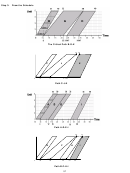 11
11 12
12