Critical-Path Analysis For Network Scheduling Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
Name
i
i
duration = d
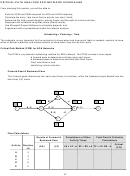
ES
LF
ES
EF=ES+d
a) Activity is early
d
TF
LS=LF-d
b) Activity is late
TF
d
LF
Total time available for the activity = LF - ES
Total Float (TF) = Total Slack = LF – EF = LS – ES = LF – ES – d
Another type of float often used in network analysis is the Free Float, which can be calculated as:
Free Float = Es (of succeeding activity) – EF (of activity in question)
The free float defines the amount of time that an activity can be delayed without taking float away
from any other activity. With free float available for an activity, a project manager knows that the
float can be used without changes the status of any non-critical activity to become critical.
Identifying Critical Activities
Critical activities are the ones having TF = 0. They form a continuous path of the critical activities
that is the longest in the network (Critical Path).
Precedence Diagram Method (PDM) for AON Networks
Sequence
1
2
3
Step
B
(3)
E (5)
A (3)
C (4)
D (6)
48
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1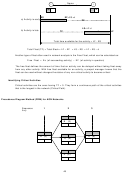 2
2 3
3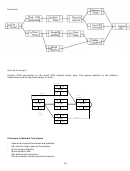 4
4 5
5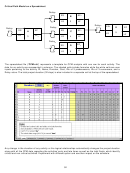 6
6 7
7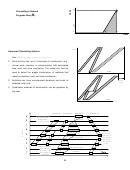 8
8 9
9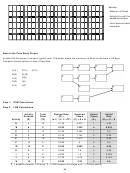 10
10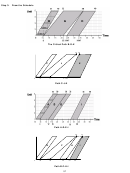 11
11 12
12