Systemd Command Vs Sysvinit: Commands Sheet
ADVERTISEMENT
Systemd SysVinit
Systemd
SysVinit
VS
Systemd Commands:
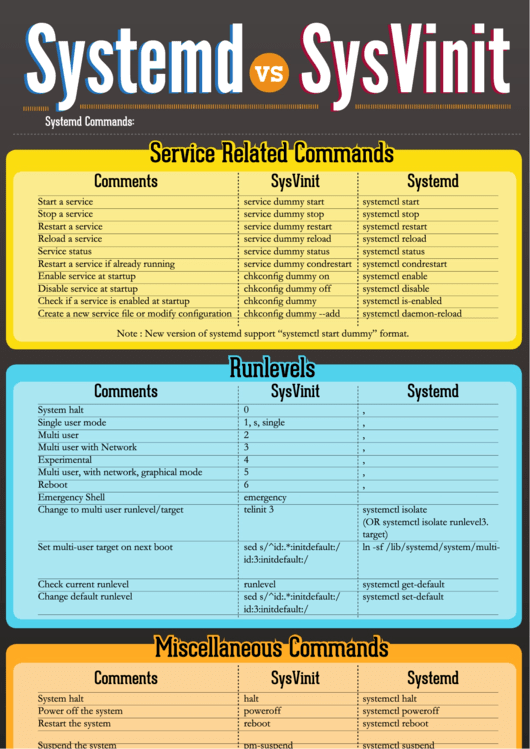
Service Related Commands
Comments
SysVinit
Systemd
Start a service
service dummy start
systemctl start dummy.service
Stop a service
service dummy stop
systemctl stop dummy.service
Restart a service
service dummy restart
systemctl restart dummy.service
Reload a service
service dummy reload
systemctl reload dummy.service
Service status
service dummy status
systemctl status dummy.service
Restart a service if already running
service dummy condrestart
systemctl condrestart dummy.service
Enable service at startup
chkconfig dummy on
systemctl enable dummy.service
Disable service at startup
chkconfig dummy off
systemctl disable dummy.service
Check if a service is enabled at startup
chkconfig dummy
systemctl is-enabled dummy.service
Create a new service file or modify configuration
chkconfig dummy --add
systemctl daemon-reload
Note : New version of systemd support “systemctl start dummy” format.
Runlevels
Comments
SysVinit
Systemd
System halt
0
runlevel0.target, poweroff.target
Single user mode
1, s, single
runlevel1.target, rescue.target
Multi user
2
runlevel2.target, multi-user.target
Multi user with Network
3
runlevel3.target, multi-user.target
Experimental
4
runlevel4.target, multi-user.target
Multi user, with network, graphical mode
5
runlevel5.target, graphical.target
Reboot
6
runlevel6.target, reboot.target
Emergency Shell
emergency
emergency.target
Change to multi user runlevel/target
telinit 3
systemctl isolate multi-user.target
(OR systemctl isolate runlevel3.
target)
Set multi-user target on next boot
sed s/^id:.*:initdefault:/
ln -sf /lib/systemd/system/multi-
id:3:initdefault:/
user.target /etc/systemd/system/
default.target
Check current runlevel
runlevel
systemctl get-default
Change default runlevel
sed s/^id:.*:initdefault:/
systemctl set-default multi-user.target
id:3:initdefault:/
Miscellaneous Commands
Comments
SysVinit
Systemd
System halt
halt
systemctl halt
Power off the system
poweroff
systemctl poweroff
Restart the system
reboot
systemctl reboot
Suspend the system
pm-suspend
systemctl suspend
Hibernate
pm-hibernate
systemctl hibernate
Follow the system log file
tail -f /var/log/messages
journalctl -f
or tail -f /var/log/syslog
Systemd New Commands
Comments
Systemd
Execute a systemd command on remote host
systemctl dummy.service start -H user@host
Check boot time
systemd-analyze or systemd-analyze time
Kill all processes related to a service
systemctl kill dummy
Get logs for events for today
journalctl --since=today
Hostname and other host related information
hostnamectl
Date and time of system with timezone and other information
timedatectl
Brought to you by LinOxide Team
Linux公社(
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1








