Unit 10 Review Chapter 10 - Blood - Anatomy And Physiology Test With Answers Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
26. What organ removes damaged or old blood cells?
Liver or spleen
27. __Sickle__ cell anemia is caused by inheritance of an abnormal type of hemoglobin that distorts the RBC's into
sickle shapes.
28. __Anemia___ is any of a number of different conditions caused by an inability to carry sufficient oxygen to the
body cells.
29. A blood clot is called a ____Thrombus________.
30. A dislodged and free floating clot is called an _____Embolus____________.
31. A low white count (under 5,000/dl of blood) caused by diseases of the immune system is called
__Leukopenia_____.
32. A substance that reacts to an antigen, usually causing them to clump together is called a/an
____Antibody_______.
33. An abnormally high white blood cell count, usually because of infection, is called _____Leukocytosis______.
34. Any substance that stimulates the production of antibodies is called a/an ____Antigen______.
35. Platelets are also called ___Thrombocytes________.
36. The clumping of antibodies and antigens is called ____Agglutination______________.
37. The iron containing protein that combines with oxygen is called ____Hemoglobin________.
38. The liquid part of the blood that has not clotted is called ___Plasma_______.
39. The major function of the RBC's is to transport ____Oxygen________.
40. The number one function of blood is _________Transportation of nutrients and waste products __________.
41. Normal blood pH is _____7.35 to 7.45___________.
42. Type A blood has the ___A_____antigen on its surface, while type B blood has the _____B_______ antigen on
its surface. Type AB blood has _______Both A and B_______ and type O blood has ___NO_____ antigens.
43. Where does hematopoiesis take place in an adult?
In the bone marrow of the pelvis, femur, and the skull bones.
44. How is RBC formation controlled? What is erythropoietin? What are factors that cause its release?
Damaged and old cells are removed by liver and spleen, but when more are needed, the kidneys, in response
to low blood oxygen levels, release erythropoietin to stimulate the bone marrow to make more RBCS. Low
oxygen levels and bleeding can lead to erythropoietin being released.
45. Describe why a person with blood type AB cannot give to a person with blood type B? Explain why blood type O
is the Universal Donor, and blood type AB is the Universal Recipient.
Blood type AB cannot give blood to a type B person because Type AB has the A antigen on its surface and it
would cause the A antibodies of the recipient to attack the transfused blood and agglutination would occur.
Type O blood is the universal donor because it lacks both A and B antigens (agglutination would not occur if
donated) whereas type AB has both A and B antigens on its surface and would have not have any reactions to
any type A and type B blood making it the universal recipient.
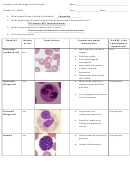
46. A hematocytoblast gives rise to two different stem cells. What are they and what cells do they
differentiate/change into?
Myeloid and lymphoid stem cells. Lymphoid stem cells become lymphocytes and myeloid stem cells from the
bone marrow give rise to erythrocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, and platelets.
47. What is thrombocytopenia?
It is a condition where there is lack of platelets in the normal blood which could lead to internal bleeding.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1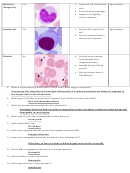 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5