Review Chemical Bonding And Molecular Geometry Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
16. Classify the following compounds as ionic or molecular (covalent):
a. C
H
covalent
c. Na
O
ionic
2
4
2
b. KF
ionic
d. SO
covalent
2
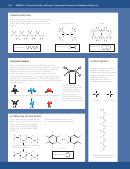
17. Illustrate the formation of an ionic bond between one atom of aluminum and three atoms of bromide
to form aluminum bromide. Include the following:
a. Draw an electron dot diagram for each atom involved.
b. Write the symbol of the noble gas each atom desires to be like.
c. Show the transfer of electrons from the metal to the non-metal using arrows.
d. Draw an electron dot diagram for the aluminum and bromide ions formed.
Al
Br
Al like Ne
Br like Kr
3+
1-
Br
[ Al ]
3 [ Br ]
Br
18. Draw structures for the following molecules. Identify their molecular geometry.
-
-
a. NF
Use 26e
c. SO
use 18e
3
2
F
N
F
polar
O
S
polar
O
F
pyramidal
bent angular 2:1 ratio (see M.G. sheet)
b. N
O
Use 16e-
d. CI
Use 32e-
2
4
I
N
N
O
polar
nonpolar
I
C
I
linear (double bond both sides)
I
tetrahedral – single bonds
19. Explain the difference between miscible and immiscible.
Miscible liquids will dissolve into
each other (isopropyl alcohol and water) and immiscible liquids will not mix together. (oil and
water)
20. What effect does hydrogen bonding and polarity have on the properties of liquids?
Hydrogen bonding is the unusually strong dipole-dipole interaction that occurs when a highly
electronegative atom (N, O, or F) is bonded to a hydrogen atom. These strong intermolecular
forces cause higher melting and boiling points, lower vapor pressure, and an increase in
surface tension and viscosity of liquids.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4