Publication 501 - Exemptions, Standard Deduction, And Filing Information - 2009 Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
U.S. Citizens or Resident Aliens
You must file Form 1040 if you owe any
Who Must File
Living Abroad
self-employment tax.
TIP
For purposes of determining whether you must
If you are a U.S. citizen or resident alien,
file a return, you must include in your gross
whether you must file a federal income tax return
income all of the income you earned or received
Filing status. Your filing status generally de-
depends on your gross income, your filing sta-
abroad, including any income you can exclude
pends on whether you are single or married. In
tus, your age, and whether you are a dependent.
under the foreign earned income exclusion. For
some cases, it depends on other factors as well.
For details, see
Table 1
and
Table
2. You also
more information on special tax rules that may
Whether you are single or married is determined
must file if one of the situations described in
apply to you, see Publication 54, Tax Guide for
as of the last day of your tax year, which is
Table 3
applies. The filing requirements apply
U.S. Citizens and Resident Aliens Abroad.
December 31 for most taxpayers. Filing status is
even if you owe no tax.
discussed in detail later in this publication.
You may have to pay a penalty if you are
Residents of Puerto Rico
required to file a return but fail to do so. If you
Age. Age is a factor in determining if you must
willfully fail to file a return, you may be subject to
file a return only if you are 65 or older at the end
Generally, if you are a U.S. citizen and a bona
criminal prosecution.
of your tax year. For 2009, you are 65 or older if
fide resident of Puerto Rico, you must file a U.S.
For information on what form to use — Form
you were born before January 2, 1945.
income tax return if you meet the income re-
1040EZ, Form 1040A, or Form 1040 — see the
quirements. This is in addition to any legal re-
instructions in your tax package.
Filing Requirements
quirement you may have to file an income tax
for Most Taxpayers
return with Puerto Rico.
Gross income. Gross income is all income
If you are a bona fide resident of Puerto Rico
you receive in the form of money, goods, prop-
You must file a return if your gross income for
for the whole year, your U.S. gross income does
erty, and services that is not exempt from tax. If
the year was at least the amount shown on the
not include income from sources within Puerto
you are married and live with your spouse in a
appropriate line in
Table
1. Dependents should
Rico. However, include in your U.S. gross in-
community property state, half of any income
see
Table 2
instead.
come any income you received for your services
defined by state law as community income may
as an employee of the United States or any U.S.
be considered yours. For a list of community
agency. If you receive income from Puerto Ri-
Deceased Persons
property states, see
Community property states
can sources that is not subject to U.S. tax, you
under Married Filing Separately, later.
must reduce your standard deduction, which
You must file an income tax return for a dece-
reduces the amount of income you can have
Self-employed persons.
If you are
dent (a person who died) if both of the following
before you must file a U.S. income tax return.
self-employed in a business that provides serv-
are true.
For more information, see Publication 570,
ices (where products are not a factor), your
Tax Guide for Individuals With Income From
gross income from that business is the gross
1. You are the surviving spouse, executor,
U.S. Possessions.
receipts. If you are self-employed in a business
administrator, or legal representative.
involving manufacturing, merchandising, or min-
2. The decedent met the filing requirements
ing, your gross income from that business is the
Individuals With Income From U.S.
described in this publication at the time of
total sales minus the cost of goods sold. To this
his or her death.
Possessions
figure, you add any income from investments
and from incidental or outside operations or
For more information, see Final Return for
If you had income from Guam, the Common-
sources.
Decedent in Publication 559.
wealth of Northern Mariana Islands, American
Samoa, or the U.S. Virgin Islands, special rules
Table 1. 2009 Filing Requirements Chart for Most Taxpayers
may apply when determining whether you must
file a U.S. federal income tax return. In addition,
THEN file a return
you may have to file a return with the individual
if your gross
possession government. See Publication 570
AND at the end of 2009 you
income was at
for more information.
IF your filing status is...
were...
*
least...
**
Dependents
single
under 65
$ 9,350
A person who is a dependent may still have to
65 or older
$10,750
file a return. This depends on the amount of the
head of household
under 65
$12,000
dependent’s earned income, unearned income,
and gross income. For details, see
Table
2. A
65 or older
$13,400
dependent may also have to file if one of the
situations described in
Table 3
applies.
married, filing jointly
***
under 65 (both spouses)
$18,700
65 or older (one spouse)
$19,800
Responsibility of parent. If a dependent
child who must file an income tax return cannot
65 or older (both spouses)
$20,900
file it for any reason, such as age, a parent,
guardian, or other legally responsible person
married, filing separately
any age
$ 3,650
must file it for the child. If the child cannot sign
qualifying widow(er) with
under 65
$15,050
the return, the parent or guardian must sign the
child’s name followed by the words “By (your
dependent child
65 or older
$16,150
signature), parent for minor child.”
Earned income. This is salaries, wages, pro-
*
If you were born before January 2, 1945, you are considered to be 65 or older at the end of 2009.
** Gross income means all income you received in the form of money, goods, property, and services that
fessional fees, and other amounts received as
is not exempt from tax, including any income from sources outside the United States or from the sale
pay for work you actually perform. Earned in-
of your main home (even if you can exclude part or all of it). Do not include any social security benefits
come (only for purposes of filing requirements
unless (a) you are married filing a separate return and you lived with your spouse at any time during
and the standard deduction) also includes any
2009, or (b) one-half of your social security benefits plus your other gross income and any tax-exempt
part of a scholarship that you must include in
interest is more than $25,000 ($32,000 if married filing jointly). If (a) or (b) applies, see the Form 1040
instructions to figure the taxable part of social security benefits you must include in gross income.
your gross income. See chapter 1 of Publication
*** If you did not live with your spouse at the end of 2009 (or on the date your spouse died) and
970, Tax Benefits for Education, for more infor-
your gross income was at least $3,650, you must file a return regardless of your age.
mation on taxable and nontaxable scholarships.
Publication 501 (2009)
Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Financial
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8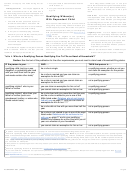 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28








