Publication 501 - Exemptions, Standard Deduction, And Filing Information - 2009 Page 5
ADVERTISEMENT
Table 3. Other Situations When You Must File a 2009 Return
State law governs whether you are married
or legally separated under a divorce or separate
maintenance decree.
If any of the four conditions listed below applied to you for 2009, you must file a
return.
Divorced persons.
If you are divorced
under a final decree by the last day of the year,
1. You owe any special taxes, including any of the following.
you are considered unmarried for the whole
year.
a. Alternative minimum tax. (See the Form 1040 instructions for line 45.)
Divorce and remarriage. If you obtain a
divorce in one year for the sole purpose of filing
b. Additional tax on a qualified plan, including an individual retirement
tax returns as unmarried individuals, and at the
arrangement (IRA), or other tax-favored account. (See Publication 590,
time of divorce you intended to and did remarry
Individual Retirement Arrangements (IRAs), and Publication 969, Health
each other in the next tax year, you and your
Savings Accounts and Other Tax-Favored Health Plans.) But if you are filing a
spouse must file as married individuals.
return only because you owe this tax, you can file Form 5329 by itself.
Annulled marriages. If you obtain a court
decree of annulment, which holds that no valid
c. Social security or Medicare tax on tips you did not report to your employer (see
marriage ever existed, you are considered un-
Publication 531, Reporting Tip Income) or on wages you received from an
married even if you filed joint returns for earlier
employer who did not withhold these taxes (see Form 8919).
years. You must file amended returns (Form
1040X) claiming single or head of household
d. Write-in taxes, including uncollected social security, Medicare, or railroad
status for all tax years affected by the annulment
retirement tax on tips you reported to your employer or on group-term life
that are not closed by the statute of limitations
for filing a tax return. The statute of limitations
insurance and additional tax on health savings accounts. (See Publication 531,
generally does not end until 3 years after your
Publication 969, and the Form 1040 instructions for line 60.)
original return was filed.
e. Household employment taxes. But if you are filing a return only because you
Head of household or qualifying widow(er)
owe these taxes, you can file Schedule H by itself.
with dependent child. If you are considered
unmarried, you may be able to file as a head of
household or as a qualifying widow(er) with a
f. Recapture taxes. (See the Form 1040 instructions for lines 44 and 60.)
dependent child. See
Head of Household
and
Qualifying Widow(er) With Dependent Child
to
2. You received any advance earned income credit (EIC) payments from your
see if you qualify.
employer. These payments should be shown in box 9 of your Form W-2. (See
Publication 596, Earned Income Credit (EIC).)
Married persons. If you are considered mar-
ried for the whole year, you and your spouse can
3. You had net earnings from self-employment of at least $400. (See Schedule SE
file a joint return, or you can file separate re-
(Form 1040) and its instructions.)
turns.
Considered married. You are considered
4. You had wages of $108.28 or more from a church or qualified church-controlled
married for the whole year if on the last day of
organization that is exempt from employer social security and Medicare taxes.
your tax year you and your spouse meet any one
(See Schedule SE (Form 1040) and its instructions.)
of the following tests.
1. You are married and living together as
husband and wife.
5. You qualify for the additional child tax
the column in the Tax Table that applies to your
credit. See the instructions in your tax
filing status.
2. You are living together in a common law
forms package for more information on this
You also use your filing status in determining
marriage that is recognized in the state
credit.
whether you are eligible to claim certain other
where you now live or in the state where
deductions and credits.
the common law marriage began.
6. You qualify for the refundable American
There are five filing statuses:
opportunity education credit. See Form
3. You are married and living apart, but not
•
8863, Education Credits.
Single,
legally separated under a decree of di-
•
vorce or separate maintenance.
7. You qualify for the health coverage tax
Married Filing Jointly,
credit. For information about this credit,
•
4. You are separated under an interlocutory
Married Filing Separately,
see Form 8885, Health Coverage Tax
(not final) decree of divorce. For purposes
•
Head of Household, and
Credit.
of filing a joint return, you are not consid-
•
ered divorced.
Qualifying Widow(er) With Dependent
8. You qualify for the refundable credit for
Child.
prior year minimum tax. See Form 8801,
Spouse died during the year. If your
Credit for Prior Year Minimum Tax — Indi-
If more than one filing status applies to you,
spouse died during the year, you are considered
viduals, Estates, and Trusts.
choose the one that will give you the lowest tax.
married for the whole year for filing status pur-
9. You qualify for the first-time homebuyer
poses.
Marital Status
credit. See Form 5405, First-Time
If you did not remarry before the end of the
Homebuyer Credit.
tax year, you can file a joint return for yourself
In general, your filing status depends on
and your deceased spouse. For the next 2
whether you are considered unmarried or mar-
years, you may be entitled to the special benefits
ried. For federal tax purposes, a marriage
described later under
Qualifying Widow(er) With
means only a legal union between a man and a
Filing Status
Dependent
Child.
woman as husband and wife.
If you remarried before the end of the tax
year, you can file a joint return with your new
You must determine your filing status before you
Unmarried persons. You are considered un-
spouse. Your deceased spouse’s filing status is
can determine your filing requirements, stan-
married for the whole year if, on the last day of
married filing separately for that year.
dard deduction (discussed later), and correct
your tax year, you are unmarried or legally sepa-
tax. You figure your correct tax by using the
rated from your spouse under a divorce or sepa-
Married persons living apart. If you live
section of the Tax Computation Worksheet or
rate maintenance decree.
apart from your spouse and meet certain tests,
Publication 501 (2009)
Page 5
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Financial
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8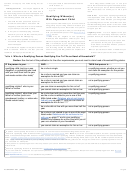 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28








