The Muscular System - Anatomy Coloring Sheet Page 7
ADVERTISEMENT
LWBK244-4102G-C04_48-69.qxd 12/11/08 6:11 PM Page 54 LWBK160-3985G-C95_1329-135#C1BC
Coloring Exercise 4-4
Energy for Working Muscles: ATP
Where do Muscles Obtain ATP?
Creatine phosphate
B
COLORING INSTRUCTIONS
Color each structure and its
• Very rapid ATP
A
production; no oxygen or glucose required
name at the same time, us-
• Muscles contain small store of creatine phosphate
ing the same color. On the
• Creatine phosphate loses phosphate group, creating creatine
C
top figure:
• ADP
accepts phosphate group, resulting in ATP
D
A
1. Color the terms ADP ,
creatine phosphate, and
• Creatine phosphate stores increased by exercise, dietary supplementation
creatine.
Anaerobic metabolism
E
2. Color the ATP molecule
• Glucose
rapidly converted into small amount of ATP
(2–3 molecules);
F
A
of this diagram bright
no oxygen
required
G
green.
• Lactic acid
produced as byproduct
H
• Glucose can come from blood or (more frequently) from glycogen
break-
I
COLORING INSTRUCTIONS
down
1. Color the glycogen
I
Aerobic metabolism
and glucose
J
E
molecules using related
• Glucose slowly converted into large amount of ATP (over 30 molecules);
colors. Note that glyco-
oxygen required
gen is actually made up
• Oxygen is stored within muscle cells attached to myoglobin
K
of many glucose mole-
• Other energy sources (amino acids, fatty acids) can also be used
cules.
2. Color the anaerobic
arrow
and the
E
Why do Muscles Need ATP?
weightlifter with the
• Power stroke
: movement of the myosin head that brings actin filaments
same color.
L
closer together
3. Color the adjacent oxy-
gen molecule
. Draw
G
• Myosin head detachment
: no ATP results in rigor mortis: myosin heads
M
a black X over it to indi-
stay attached, muscle cannot relax
cate that oxygen is not
• Calcium reuptake
N
used.
Calcium reuptake into endoplasmic reticulum necessary for muscle relax-
•
4. Color the two ATP mole-
ation
cules
and the lactic
A
Occurs by active transport
•
acid
.
H
COLORING INSTRUCTIONS
1. Color the aerobic arrow
and the cross-country
J
skier with the same
color.
2. Color the adjacent oxy-
gen molecules
and
G
myoglobin
K
.
3. Color the ATP molecules
. Not all of the ATPs
A
are shown—one glucose
molecule can produce
over 30 ATPs.
COLORING INSTRUCTIONS
Color the terms
to
and
L
N
the accompanying cartoons.
54
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1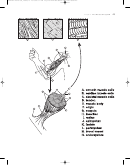 2
2 3
3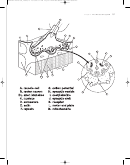 4
4 5
5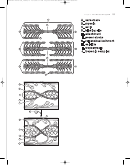 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9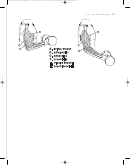 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13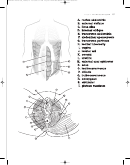 14
14 15
15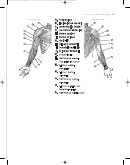 16
16 17
17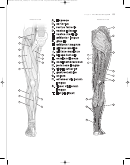 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22