Enthalpy Of Reaction And Calorimetry Worksheet Page 10
ADVERTISEMENT
Hess’ Law with Bond Energies/Enthalpies Worksheet
Hess' Law for bond enthalpies is:
H rxn = Σ BE reactant bonds broken Σ BE product bonds broken
Use the Bond Energy values from the Reference Sheet
eg. Hydrogenation of double and triple bonds is an important industrial process. Calculate (in kJ) the
standard enthalpy change ΔH for the hydrogenation of ethyne (acetylene) to ethane:
H−C≡C−H (g)
+
2 H 2 (g)
H 3 C−CH 3 (g)
H rxn = Σ BE reactant bonds broken Σ BE product bonds broken
= [2 C−H bonds + 1 C≡C bond + 2 H−H bonds] [6 C−H bonds + 1 C−C bond
)] [6
= [2
(413
) + 1
(839
) + 2
(432
(413
) + 1
(347
mol
kJ/mol
mol
kJ/mol
mol
kJ/mol
mol
kJ/mol
mol
)]
kJ/mol
= 2529 kJ 2825 kJ
= -296 kJ
= [1 C≡C bond + 2 H−H bonds] [4 C−H bonds + 1 C−C bond] = -296 kJ
OR
Using bond enthalpies, calculate the reaction enthalpy (ΔH) for:
1.
CH 4 (g)
+
Cl 2 (g)
CH 3 Cl (g)
+
HCl (g)
Calculate ΔH for this reaction:
2.
H 2 C=CH 2 (g)
+
H 2 O (l)
CH 3 -CH 2 -OH (l)
3. Calculate ΔH for this reaction:
2 CH 3 OH (l)
+
3 O 2 (g)
2 CO 2 (g)
+
4 H 2 O (g)
4. Calculate the bond energy of the Cl-F bond using the following data:
ΔH rxn = −108 kJ
Cl 2
+
F 2
2ClF
5. Ammonia reacts with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide and steam, as follows:
4 O−N=O (g)
4 NH 3 (g)
+
7 O 2 (g)
+
6H 2 O (g)
6. Calculate ΔH for this reaction:
2 CH 3 CH=CH 2
+
9 O 2
6 CO 2
+
6 H 2 O
7. Considering bonds broken and formed ONLY, what is the enthalpy change for the following reaction:
C 40 H 82
C 16 H 34
+
2 C 12 H 24 (cyclic)
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1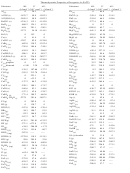 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14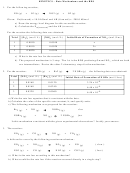 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20