Enthalpy Of Reaction And Calorimetry Worksheet Page 19
ADVERTISEMENT
4. The following results were obtained when the reaction represented below was studied at 25˚C.
2 ClO 2(g)
+
F 2(g)
2 ClO 2 F (g)
Experiment [ClO 2 ] i (mol/L) [F 2 ] i (mol/L) Rate of Increase of [ClO 2 F] i (mol/L •s)
-3
1
0.010
0.10
-3
2
0.010
0.40
-3
3
0.020
0.20
a) Write the rate law expression for the reaction above.
b) Calculate the numerical value of the rate constant and specify the units.
c) In experiment 2, what is the initial rate of decrease of [F 2 ]?
d) Which of the following reaction mechanisms is consistent with the rate law developed in (a). Justify
your choice.
I. ClO 2
+
F 2
ClO 2 F 2
(fast)
ClO 2 F 2
ClO 2 F
+
F
(slow)
ClO 2
+
F
ClO 2 F
(fast)
II. F 2
2 F
(slow)
2 (ClO 2
+
F
ClO 2 F) (fast)
5. Freon gases, e.g. CCl 2 F 2 (g) , from leaking air conditioners and refrigeration units also make their way
into the upper atmosphere.. These gases catalyze the destruction of ozone.
CClF 2 • (g)
ClO • (g)
CCl 2 F 2 (g)
+
O 3 (g)
+
+
O 2 (g)
Where, Cl • , is a reaction intermediate. Propose a mechanism for this reaction.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14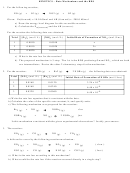 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20