Birth Control Chart
ADVERTISEMENT
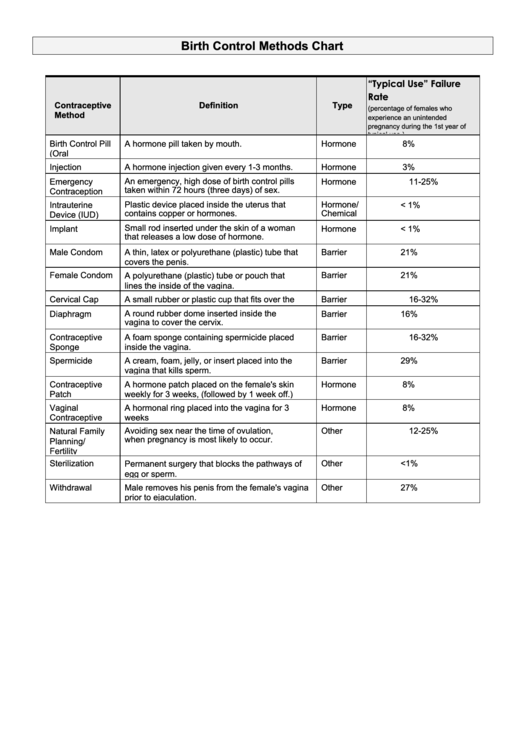
Birth Control Methods Chart
“Typical Use” Failure
Rate
Contraceptive
Definition
Type
(percentage of females who
Method
experience an unintended
pregnancy during the 1st year of
typical use.)
Birth Control Pill
A hormone pill taken by mouth.
Hormone
8%
(Oral
Contraceptive)
Injection
A hormone injection given every 1-3 months.
Hormone
3%
An emergency, high dose of birth control pills
Emergency
Hormone
11-25%
taken within 72 hours (three days) of sex.
Contraception
Plastic device placed inside the uterus that
Hormone/
Intrauterine
< 1%
contains copper or hormones.
Chemical
Device (IUD)
Small rod inserted under the skin of a woman
Implant
Hormone
< 1%
that releases a low dose of hormone.
Male Condom
A thin, latex or polyurethane (plastic) tube that
Barrier
21%
covers the penis.
Female Condom
A polyurethane (plastic) tube or pouch that
Barrier
21%
lines the inside of the vagina.
Cervical Cap
A small rubber or plastic cup that fits over the
Barrier
16-32%
cervix.
A round rubber dome inserted inside the
Diaphragm
Barrier
16%
vagina to cover the cervix.
Contraceptive
A foam sponge containing spermicide placed
Barrier
16-32%
Sponge
inside the vagina.
Spermicide
A cream, foam, jelly, or insert placed into the
Barrier
29%
vagina that kills sperm.
Contraceptive
A hormone patch placed on the female's skin
Hormone
8%
Patch
weekly for 3 weeks, (followed by 1 week off.)
Vaginal
A hormonal ring placed into the vagina for 3
Hormone
8%
Contraceptive
weeks
Ring
(followed by 1 week off).
Avoiding sex near the time of ovulation,
Natural Family
Other
12-25%
when pregnancy is most likely to occur.
Planning/
Fertility
Awareness
Sterilization
Permanent surgery that blocks the pathways of
Other
<1%
Method
egg or sperm.
Withdrawal
Male removes his penis from the female's vagina
Other
27%
prior to ejaculation.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Medical
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5