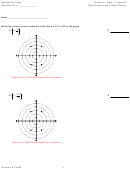
Polar Coordinates And Complex Numbers Worksheets With Answers - Math 611b Page 18
ADVERTISEMENT
SCO: By the end of grade
Elaborations - Instructional Strategies/Suggestions
12, students will be
Complex Numbers in Polar Form (9.6)
expected to:
Students will be expected to convert complex numbers from rectangular
to polar form and vice versa.
A26 translate between
Students should be familiar with the following concepts:
For complex numbers in rectangular form:
polar and rectangular
< Argand Plane
coordinates on the
< real axis, imaginary axis
complex plane
< absolute value of a complex number.
=
+
2
2
z
a
b
If z = a + bi, then
C88 represent complex
This absolute value represents the distance from zero on the complex
numbers in a variety
plane.
of ways
For complex numbers in polar form:
< modulus, r (absolute value of the complex number)
2
< argument,
(amplitude of the complex number or the angle between r
2
B
and the zero line)
Note: Replacing
with
θ
θ
θ
=
+
yields Euler’s Equation;
i
e
cos
i
sin
Euler’s Formula states that
π
π
π
=
+
i
e
cos
i
sin
θ
θ
θ
θ
=
+
=
=
< z
i
r
(cos
i
sin )
rcis
re
π
= −
i
e
1
π
+ =
i
e
1 0
Note: If a complex number
is in rectangular form, then
plot it on a rectangular
coordinate plane.
Ex 4 p.588: Express ! 3 + 4i in polar
form.
If it is in polar form, graph
Using the TI-83: enter ! 3 + 4i math < < CPX 7: < Polar enter
it on a polar coordinate
plane.
enter
or 5 cis 2.21
To convert to rectangular form press math < < CPX 6: < Rect enter ...
18
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46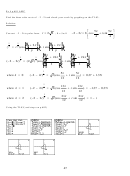 47
47 48
48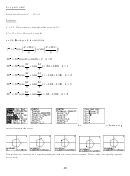 49
49 50
50