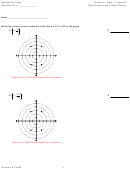
Polar Coordinates And Complex Numbers Worksheets With Answers - Math 611b Page 41
ADVERTISEMENT
The Development of Number Systems
The Egyptians invented the number system we use today replacing the Roman numeral system
making computations much simpler. Once people started borrowing gardening implements from their
neighbours, the need arose for negative numbers. When a hunter tried to share with his 5 friends the 3
geese he had bagged , then a need for fractions was born (either that or he didn’t tell some of his friends
! 5 = 0 needed to be dealt with
2
about his good fortune). Once algebra came into play, problems like x
using irrational numbers. These number systems taken together completely filled the number line (the
ú
real number line
).
All seemed right with the world until the Renaissance when some troublemaker looked for a
2
solution to x
+ 1 = 0. This created a problem because any real number when squared gives a result
greater than or equal to zero. To a chorus of protests from many of the prominent mathematicians of the
i =
−1
day, the number
was defined. These objecting mathematicians coined the phrase
“
imaginary number ” to voice their opposition. An important property of this number is that when squared
= −
2
i
1
it yields a negative result;
.
It was evident that numbers like 2i, 5 ! 4i, etc. were very useful, but there was no way of
representing these numbers on the real number line. The solution to this dilemma was put forth by a
Swiss mathematician, Jean Robert Argand. He placed an imaginary number line at right angles to the real
number line. This is called the Argand Plane.
For all real numbers a,b the number a + bi is a complex number. The letter, C , is used to
represent the set of complex numbers. We can represent a complex number z = a + bi as a vector on the
Cartesian coordinate plane or the Argand plane.
=
−
z
a
bi
T
he conjugate of a complex number z = a + bi is
.
Thus 4 ! 3i is the conjugate of 4 + 3i.
The modulus(magnitude), r, or absolute value of a complex number z = a + bi is
=
=
+
2
2
r
z
a
b
.
This is a measure of the length of the vector z = a + bi.
41
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46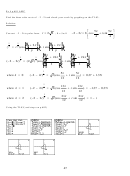 47
47 48
48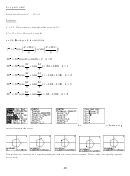 49
49 50
50