Electrochemistry Worksheet With Answers Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
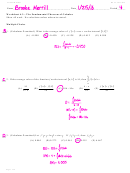
mcdonald (pam78654) – HW 10: Electrochemistry – laude – (89560)
2
2. II
The reaction
+
2+
2 Ag
(aq) + Fe(s) → Fe
(aq) + 2 Ag(s)
3. I, II
taking place in a battery generates a current
4. II, III
of 2 amp. How much Fe(s) is consumed in 1
hour?
5. I, III correct
1. 1.04 g
6. I
2. 3.46 g
7. III
Explanation:
3. 8.32 g
By definition and by convention, the stan-
dard cell potential of an electrolytic cell is less
4. 4.16 g
than zero, and the cathode is attributed a
negative sign.
5. 2.08 g correct
Explanation:
006
10.0 points
i = 2 A
t = 1 h
The half equation of interest is
How long would a current of 10 mA take
5+
to produce 0.096 g of Mo(s) from Mo
(aq)?
2+
Fe(s) → Fe
+ 2 e
1. 964, 850 s
and the total charge is
60 min
60 sec
q = (2 A) (1 h)
= 7200 C .
2. 9, 648, 500 s
1 h
1 min
We can then convert this charge to num-
3. 48, 242.5 s correct
ber of electrons and finally the amount of Fe
consumed:
1 mol e
1 mol Fe
4. 4, 824, 250 s
(7200 C)
×
96485 C
2 mol e
5. 9, 648.5 s
55.847 g Fe
×
= 2.08374 g Fe
1 mol Fe
6. 48, 242, 500 s
008
10.0 points
Explanation:
The figure represents a reaction at 298 K.
This is a 4 electron process.
A
1 mol
(0.096 g Mo(s))
= 0.001 mol Mo(s)
B
96 g
E
G
10 mA = 0.01 A
C D
It
= n
p
N
F
e
n
N
F
rxn progress
p
e
t =
I
Based on the figure, the standard voltage is
0.001 · 5 · 96, 485
=
0.01
1. positive. correct
= 48, 242.5 s
2. negative.
007
10.0 points
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5