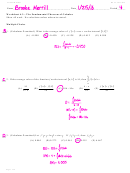
Electrochemistry Worksheet With Answers Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
mcdonald (pam78654) – HW 10: Electrochemistry – laude – (89560)
4
+
Ag
+ e → Ag
E
◦
= +0.80
Voltmeter
red
2+
Fe
+ 2 e → Fe
E
◦
= 0.44
red
1.10 V
and what type cell is it?
e
e
V
+
1. Ag(s) | Ag
(aq); an electrolytic cell
Copper
Zinc
(Anode)
(Cathode)
2. Not enough information is provided.
Salt
bridge
2+
3. Fe
(aq) | Fe(s); an electrolytic cell cor-
to carry
rect
ions
2+
4. Fe
(aq) | Fe(s); a battery
2+
2+
1 M Zn
(aq)
1 M Cu
(aq)
+
In this electrochemical cell, what is the re-
5. Ag(s) | Ag
(aq); a battery
duction half reaction?
2+
1. Zn(s) → Zn
(aq) + 2 e
Explanation:
2+
2. Cu
(aq) + 2 e → Cu(s) correct
The diagram A | B || C | D is read as follows:
A → B + n e (oxidation)
2+
3. Zn
(aq) + 2 e → Zn(s)
C + m e → D (reduction)
Since reduction occurs at the cathode, the
2+
4. Cu(s) → Cu
(aq) + 2 e
2+
cathode is Fe
(aq) | Fe(s).
◦
To determine the cell type, calculate E
cell:
Explanation:
2+
2+
Zn(s) + Cu
(aq) → Zn
(aq) + Cu(s)
Reduction occurs at the cathode. In this
cell the reduction half reaction is
+
2 Ag(s) → 2 Ag
(aq) + 2 e
2+
Cu
(aq) + 2 e → Cu(s)
E
◦
= 0.80 V
anode
2+
2+
Cu
cations are attracted to the solid Cu
Fe
+ 2 e → Fe
electrode where they are reduced to Cu(s).
◦
E
= 0.44 V
cathode
2+
+
2 Ag(s) + Fe
→ 2 Ag
(aq) + Fe
015
10.0 points
E
◦
= 1.24 V
What is the E
◦
of
cell
cell
2+
4+
3+
Zn(s) | Zn
(aq) || Ce
(aq) | Ce
(aq)
2+
Zn
+ 2 e → Zn
◦
= 0.76
E
red
4+
3+
Since E
◦
cell is negative, the reaction is not
Ce
+ e → Ce
◦
= +1.61
E
red
spontaneous; potential has to be applied to
the cell to enable this reaction to occur; i.e.,
1. +1.61
an electrolytic cell.
0.85
2.
014
10.0 points
2.37
3.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5