Quadratic Equations Worksheet With Answer Key Page 6
ADVERTISEMENT
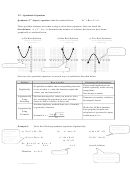
B. Quadratic inequalities and their solution sets.
If we have a quadratic inequality, we can often solve it if the algebraic expression can
be rewritten in factorial form. The following example may make the concept clear.
Example:
2
Solve the inequality x
– 3x + 2 ≤ 0.
Solution:
2
we have x
– 3x + 2 ≤ 0.
or (x-2)(x-1) ≤ 0.
From this we can say that the number line is divided into three parts cutting at
x = 1 and x = 2. So the possible inequalities are x<1, 1<x<2 and x>2. One or two
of them is the required solution of the given inequality. We need to add equal
sign to the required solution because there is ≤ sign which contains equality also.
For x < 1, the value of x – 2 is always –ve and x-1 is also –ve. ... ... ... [a]
So, the product of x – 2 and x – 1 is +ve
For 1<x<2, the value of x – 2 is always –ve and x-1 is +ve. ... ... ... [b]
So, the product of x – 2 and x – 1 is -ve
For x>2, the value of x – 2 is always +ve and x-1 is also +ve. ... ... ... [c]
So, the product of x – 2 and x – 1 is +ve
Since we need the product negative or equal to zero [(x-2)(x-1) ≤ 0]; the required
solution is of type [b] with equality.
Hence the required solution is 1 ≤ x ≤ 2.
This can be summarized int he following table:
x<1
1<x<2
x>2
x-2
-ve
-ve
+ve
x-1
-ve
+ve
+ve
(x-1)(x-2)
+ve
-ve
+ve
For (x-1)(x-2)<0, the middle column gives the solution area.
Hence for (x-1)(x-2) ≤ 0, the solution set is 1 ≤ x ≤ 2.
Class works.
C.
2
1. Form a quadratic equation whose roots are squares of the roots of x
– 2x - 3 = 0
2
2. Form a quadratic equation whose roots are thrice the roots of x
– 2x - 5 = 0
3. Solve the inequalities given below.
2
2
2
i) x
– 3x + 2 ≤ 0
ii) x
– 3x - 4 ≥ 0
iii) 2x
– 3x - 2 ≤ 0
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7