Trigonometric Ratios Worksheet Page 8
ADVERTISEMENT
1.3 Trigonometry of Angles
KEY CONCEPTS
• Exactly two angles between 0° and 360° have the same
y
y
sine ratio.
b
__
For example, sin = sin (10° − ) =
r
(�a, b)
(�a, b)
(a, b)
(a, b)
• Exactly two angles between 0° and 360° have the same
r
r
cosine ratio.
180°�
180°�
a
__
x
x
For example, cos = cos (360° − ) =
r
180°�
180°�
360°�
360°�
• Exactly two angles between 0° and 360° have the same
(�a, �b)
(�a, �b)
(a, �b)
(a, �b)
tangent ratio.
b
__
For example, tan = tan (10° + ) =
a
Example
4
__
, determine , where 0 ≤ ≤ 360°. °. .
Given cos =
5
Then, determine sin and tan .
Solution
4
__
.
Determine the measure of angle in quadrant I for which cos =
5
4
__
cos =
5
(
)
4
__
∠ = c os
−1
5
= 36.69…°
≐ 36.9°
The cosine ratio is positive in quadrants I and IV, so there is another angle for
4
__
which cos =
5 in quadrant IV.
∠ = 360° ° − 36.9° °
= 323.1° °
4
__
Given cos =
5 , the angle is approximately 37° or 323°.
° or 323°.
323°. °.
4
__
If cos =
5 , x = 4 and r = 5. Determine y.
2
= x
2
+ y
2
r
2
= ( 4)
2
+ y
2
5
2
25 = 16 + y
2
9 = y
±3 = y
Write the sine and tangent ratios for ∠.
3
3
__
__
sin = ±
tan = ±
4
5
MHR • Chapter 1 97-0-07-09093-2
Printer Pdf
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3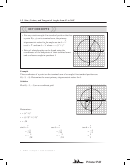 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22








