Chemistry 152 Chemistry Worksheet With Answers Page 7
ADVERTISEMENT
The pK
= pH at ½ equivalence. Half equivalence is 17.5 mL base added. The pH of the
a
solution is 4 at 17.5 mL added, so the pK
= 4.
a
16.56 Wite balanced equations and expressions for K
for the dissolution of each ionic
sp
compound:
a. CaCO
3
2+
2-
(s) ↔ Ca
CaCO
(aq) + CO
(aq)
3
3
2+
2-
K
= [Ca
][CO
]
sp
3
b. PbCl
2
2+
-
(s) ↔ Pb
PbCl
(aq) + 2 Cl
(aq)
2
2+
-
2
K
= [Pb
][Cl
]
sp
c. AgI
AgI (s) ↔ Ag
+
-
(aq) + I
(aq)
+
-
K
=[Ag
][I
]
sp
16.60 Use the given molar solubilities in pure water to calculate K
for each compound.
sp
-5
a. BaCrO
; molar solubility = 1.08x10
M
4
-5
b. Ag
SO
; molar solubility = 1.55x10
M
2
3
-8
c. Pb(SCN)
; molar solubility = 2.22x10
M
2
SOLUTION:
It all stems from the K
sp
2+
2-
2
a. K
= [Ba
][CrO
] = (S)(S) = S
sp
4
-5
2
-10
K
= (1.08x10
)
=1.17x10
sp
+
2
2-
2
-5
2
-5
-14
b. K
= [Ag
]
[SO
] = (2S)
(S) = (2x1.55x10
)
(1.55x10
) = 1.49x10
sp
3
2+
-
2
2
-8
-8
-23
c. K
= [Pb
][SCN
]
= (S)(2S)
= (2.22x10
)(2x2.22x10
)=4.38x10
sp
-36
16.66 Calculate the molar solubility of MX (K
= 1.27x10
) in
sp
a. pure water
It’s an equilibrium problem, I’m guessing it has 3 parts:
2+
2-
↔
MX(s)
M
(aq)
+ X
(aq)
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7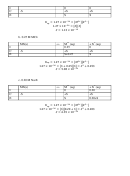 8
8








