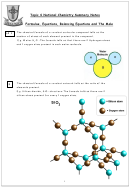
Chemical Formula Worksheet
ADVERTISEMENT
BASIC NOMENCLATURE
A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
1.
Give examples of, and recognize when given the structure, representatives of the
following classes of compounds.
Alkyl halides (1°, 2°, 3°)
Alcohols (1°, 2°, 3°), ethers
Amines (1°, 2°, 3°), amides, nitriles
3
2.
Classify carbons and hydrogens attached to sp
carbons as 1°, 2°, or 3°.
3.
Give the IUPAC names of open-chain alkanes, alkenes (including cis and trans), alkynes,
alkyl halides, and alcohols having a longest chain of ten carbons or less when given the
structure, and draw the structure given the name. The unbranched alkanes whose names
are the basis of this are:
methane (1 carbon)
hexane (6 C’s)
ethane (2 C’s)
heptane (7 C’s)
propane (3 C’s)
octane (8 C’s)
butane (4 C’s)
nonane (9 C’s)
pentane (5 C’s)
decane (10 C’s)
The names of the groups you must be able to recognize and draw are:
methyl, ethyl, propyl, butyl, pentyl, hexyl, heptyl, octyl, nonyl, decyl (the
unbranched groups)
isopropyl
isobutyl, sec-butyl, tert-butyl
neopentyl
vinyl and allyl
4.
Give the IUPAC name when given the structure, and give the structure given the IUPAC
name, of monocyclic alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, and alkyl halides having rings
containing 3-10 carbons. These compounds may also contain halogen atoms and side
chains.
5.
Give the IUPAC name when given the structure, and draw the structure given the name,
of bicyclic alkanes. These alkanes may have alkyl groups or halogen atoms as
substituents.
6.
Give the common name when given the structure, and give the structure when given the
common name, of simple alcohols and alkyl halides. In the system used here compounds
are named by first naming the alkyl group and then naming the functional group (e. g.
ethyl alcohol, neopentyl bromide).
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11