Chemical Indicators Worksheet
ADVERTISEMENT
C h e m g u i d e – q u e s t i o n s
INDICATORS
1. Methyl orange is an indicator commonly used in certain acid-base titrations. It exists in two forms,
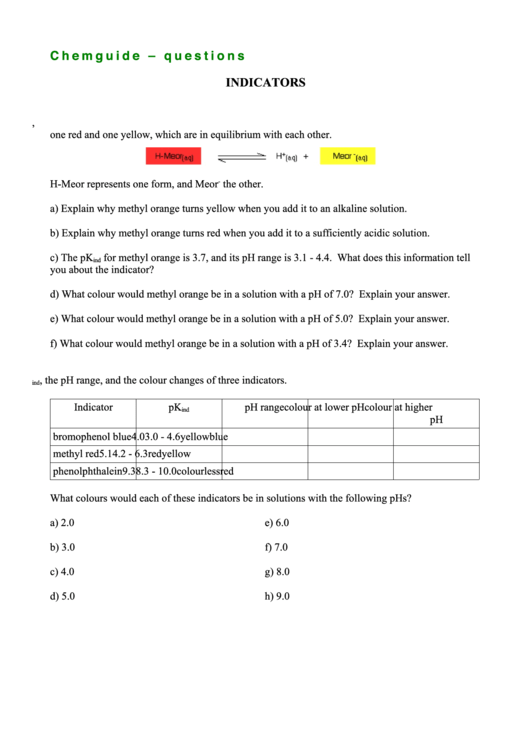
one red and one yellow, which are in equilibrium with each other.
H-Meor represents one form, and Meor
-
the other.
a) Explain why methyl orange turns yellow when you add it to an alkaline solution.
b) Explain why methyl orange turns red when you add it to a sufficiently acidic solution.
c) The pK
for methyl orange is 3.7, and its pH range is 3.1 - 4.4. What does this information tell
ind
you about the indicator?
d) What colour would methyl orange be in a solution with a pH of 7.0? Explain your answer.
e) What colour would methyl orange be in a solution with a pH of 5.0? Explain your answer.
f) What colour would methyl orange be in a solution with a pH of 3.4? Explain your answer.
2. The table shows pK
, the pH range, and the colour changes of three indicators.
ind
Indicator
pK
pH range
colour at lower pH
colour at higher
ind
pH
bromophenol blue
4.0
3.0 - 4.6
yellow
blue
methyl red
5.1
4.2 - 6.3
red
yellow
phenolphthalein
9.3
8.3 - 10.0
colourless
red
What colours would each of these indicators be in solutions with the following pHs?
a) 2.0
e) 6.0
b) 3.0
f) 7.0
c) 4.0
g) 8.0
d) 5.0
h) 9.0
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3








