Chemistry 3411 Solutions Worksheet - Georgia Institute Of Technology - 2010 Page 8
ADVERTISEMENT
CHEM 3411, Fall 2010
Solution Set 2
∫
T
f
∆H
=
C
dT
p
T
∫
i
T
f
= C
dT
p
T
i
= C
(T
T
)
p
f
i
= C
∆T
p
Using heat capacities from our textbook we can calculate the enthalpy of heating the 2 moles of NO
(g) and cooling
2
1 mole of N
O
(g).
2
4
= ν × C
∆H
∆T (Cool NO
(g))
cool
p
2
= 2 × 37.20 J ¨ ¨ ¨
× (298 & & K
373 & & K)
1
1
K
mol
1
= =
5.5800 kJ mol
= ν × C
∆H
∆T (Heat N
O
(g))
heat
p
2
4
= 1 × 77.28 J ¨ ¨ ¨
1
× (373 & & K
298 & & K)
1
K
mol
1
= = 5.7960 kJ mol
(Note that in these last two expressions the reaction coefficients are exact quantities and don’t affect number of
significant figures.)
In the original solution sets the temperatures were swapped which changed the signs of these enthalpies.
The enthalpy of the reaction at the standard temperature of T = 298 can be calculated from enthalpies of formation.
∑
∑
⊖
⊖
⊖
∆
H
=
ν
∆
H
ν
∆
H
r
p
f
r
f
p
r
Products
Reactants
= 1 × 9.16 kJ mol
1
2 × 33.18 kJ mol
1
1
=
57.2000 kJ mol
Summing these enthalpies gives the reaction enthalpy at the non-standard temperature
⊖
⊖
∆
H
(at T = 373 K) = ∆H
+ ∆
H
(at T = 298 K) + ∆H
r
cool
r
heat
1
1
1
=
5.5800 kJ mol
+ 57.2000 kJ mol
+ 5.7960 kJ mol
1
=
56.9840 kJ mol
Solution
⊖
1
∆
H
(at T = 373 K) =
56.98 kJ mol
r
8
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9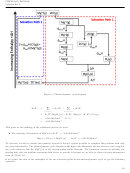 10
10 11
11 12
12








