Level Chemistry Transition Unit Worksheet With Answer Key - Healthcote School Page 10
ADVERTISEMENT
9
Reacting Mass calculations
Task 8:
Use A
values given in task 7 for this exercise. Answer in the space provided. Show your working.
r
1 What mass of hydrogen is needed to react with 40 g of copper oxide?
CuO + H
→ Cu + H
O
2
2
Moles CuO = 0.503, moles H
= 0.503, mass H
= 1.01 g.
2
2
2 What mass of sulfur trioxide is formed from 96 g of sulfur dioxide?
2 SO
+ O
→ 2 SO
2
2
3
Moles SO
= 1.5, moles SO
= 1.5, mass SO
= 120 g
2
3
3
3 What mass of carbon monoxide is needed to react with 480 g of iron oxide?
Fe
O
+ 3 CO → 2 Fe + 3 CO
2
3
2
Moles Fe
O
= 3, moles CO = 9, mass CO = 252 g.
2
3
4 What mass of oxygen is needed to react with 8.5 g of hydrogen sulfide (H
S)?
2
2 H
S + 3 O
→ 2 SO
+ 2 H
O
2
2
2
2
Moles H
S = 0.25, moles O
= 0.375, mass O
= 12 g
2
2
2
5
What mass of oxygen is required to oxidise 34 g of ammonia (NH
) to nitrogen monoxide (NO)?
3
4 NH
+ 5 O
→ 4 NO + 6 H
O
3
2
2
Moles NH
= 2, moles O
= 2.5, mass O
= 80
g.
3
2
2
6
5.00 g of hydrated sodium sulfate crystals (Na
SO
.nH
O) gave 2.20 g of anhydrous sodium
2
4
2
sulfate on heating to constant mass. Work out the relative formula mass (M
) of the hydrated
r
sodium sulfate and the value of n.
Na
SO
.nH
O → Na
SO
+ n H
O
2
4
2
2
4
2
Moles Na
SO
= 0.0155, moles Na
SO
.nH
O = 0.0155, M
Na
SO
.nH
O = 322.7, n = 10.
r
2
4
2
2
4
2
4
2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11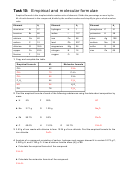 12
12 13
13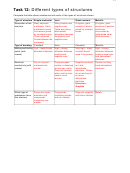 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17