Enthalpy Worksheet With Answers Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
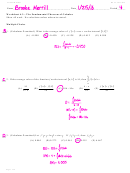
Answer
+0.533kJ/g N
O
2
3
0.533kJ/g (76.01g/mol) = +40.5kJ/mol
N
O
→ → → → NO
+ NO
∆ ∆ ∆ ∆ H = +40.5kJ
2
3(g)
(g)
2(g)
4. What is the enthalpy change when 12.8g H
reacts with excess Cl
to form HCl
?
2(g)
2(g)
(g)
H
+ Cl
→ 2HCl
∆H = -184.6kJ
2(g)
2(g)
(g)
Answer
12.8g H
/ 2.016g/mol = 6.35mol H
2
2
3
6.35mol H
(-184.6kJ/mol H
) = -1.17x10
kJ
2
2
o
5. What volume of CH
, measured at 25
C and 745Torr, must be burned in excess
4(g)
6
oxygen to release 1.00x10
kJ of heat to the surroundings?
CH
+ 2O
→ CO
+ 2H
O
∆H = -890.3kJ
4(g)
2(g)
2(g)
2
(l)
Answer
There is 890.3kJ given off for every mole of CH
burned, therefore
4
6
the moles of CH
needed are 1.00x10
kJ/(890.3kJ/mol) = 1123mol CH
4
4
o
4
V = nRT/P = (1123mol)(.0821)(25
C + 273.15)/(745/760) = 2.80x10
L CH
4
Calorimetry
1. Calculate the heat capacity of a sample of brake fluid if the sample must absorb 911J
o
o
of heat for its temperature to rise from 15
C to 100
C.
Answer
o
C = q/∆T = 911/(100-15) = 10.7J/
C
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6