Enthalpy Worksheet With Answers Page 5
ADVERTISEMENT
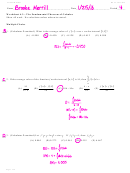
Answer:
C
H
+ 3O
2CO
+ 2H
O
2
4(g)
2(g)
2(g)
2
(l)
(4CO
+ 6H
O
2C
H
+ 7O
)/2 (flip equation and divide by 2)
2(g)
2
(l)
2
6(g)
2(g)
(2H
+ O
2H
O
)/2 (divide by 2)
2(g)
2(g)
2
(l)
C
H
+ 3O
2CO
+ 2H
O
∆H = -1410.9kJ
2
4(g)
2(g)
2(g)
2
(l)
2CO
+ 3H
O
C
H
+ 7/2 O
)
∆H = 1559.7kJ
2(g)
2
(l)
2
6(g)
2(g)
H
+ ½ O
H
O
∆H = -285.8kJ
2(g)
2(g)
2
(l)
Resulting Equation:
C
H
+ H
C
H
∆ ∆ ∆ ∆ H = -137.0kJ
2
4(g)
2(g)
2
6(g)
Standard Enthalpy of Formation
o
1. Use data from table 6.2 (p257) to calculate ∆H
for the combustion of butane gas,
C
H
, to produce gaseous carbon dioxide and liquid water.
4
10
Answer:
2C
H
+ 13O
8CO
+ 10H
O
4
10(g)
2(g)
2(g)
2
(l)
Using
o
o
o
∆H
= Σν
x ∆H
(products) - Σν
x ∆H
(reactants)
p
f
r
f
[10(-285.8kJ/mol) + 8(-393.5kJ/mol)] – [2(-125.7kJ/mol) + 13(0kJ/mol)]
-6006.0 – (-251.4) = -5754.6kJ
2. The combustion of thiophene, C
H
S
, a compound used in the manufacture of
4
4
(l)
pharmaceuticals, produces carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide gases and liquid water. The
enthalpy change in the combustion of one mole of C
H
S
is -2523kJ. Use this
4
4
(l)
o
information and date from Table 6.2 to establish ∆H
for C
H
S
.
f
4
4
(l)
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6