3-D Shapes, Weight, Volume, And Capacity Worksheet With Answers - Lesson 11.7 Unit 11 Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
Student Page
Date
Time
WHOLE-CLASS
Measuring Capacity in
ACTIVITY
LESSON
Comparing Capacities
11 7
Metric Units
1.
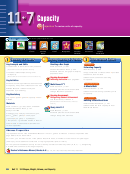
Shade in the appropriate amount to show the capacity of each of your containers.
Answers vary.
a.
b.
c.
2 L
2 L
2 L
(Math Journal 2, p. 305; Student Reference Book, p. 137)
1 L
1 L
1 L
Tell students that a liter is a metric unit of capacity. Liquids such
as water, soft drinks, and fuel are often measured in liters. Smaller
Container
Container
Container
d.
e.
f.
Circle the container
amounts of liquid are often measured in milliliters. Have
2 L
2 L
with the largest
capacity. Was your
students read Student Reference Book, page 137 and discuss the
prediction accurate?
1 L
1 L
essay with a partner.
Container
Container
Review the relationship between liters and milliliters (1 liter = 1,000
Units of Capacity
milliliters). Show students the eyedropper and explain that it holds
U.S. Customary
Metric
20 drops of water, which is equivalent to 1 milliliter. Then show them
1 gallon (gal) = 4 quarts (qt)
1,000 milliliter (mL) = 1 liter (L)
_
1
1 quart (qt) = 2 pints (pt)
1 milliliter (mL) =
liter (L)
1,000
the 1-liter pitcher and explain that this is 1 liter, or 1,000 milliliters.
1 pint (pt) = 2 cups (c)
1 pint (pt) = 16 fluid ounces (fl oz)
Explain that 1,000 eyedroppers full of water are needed to fill the
2.
Use the conversion table above to solve the problems.
1-liter pitcher. Record the following number sentence on the board to
12
8000
a.
6 qt =
b.
mL = 8 L
pt
illustrate the relationship between these two metric units:
3
6.450
c.
pt = 48 fl oz
d.
6,450 mL =
L
_
1
2
500
e.
10 qt =
2
f.
mL = 0.500 L
gal
1 liter (L) = 1,000 milliliters (mL)
64
0.032
4 gal =
32 mL =
g.
c
h.
L
Math Journal 2, p. 305A
Now have students complete journal page 305 to practice
determining the appropriate unit for measuring capacity.
305A-305B_EMCS_S_MJ2_G4_U11_576426.indd 305A
3/16/11 11:14 AM
WHOLE-CLASS
Setting up a Liter and
ACTIVITY
Milliliter Museum
Introduce a project to explore a museum of objects that have
different capacities measured in milliliters and liters. Use index
cards to label objects in the museum with their capacities. The
measuring tools available will determine the range of capacities.
Keep a variety of measuring tools near the Liter and Milliliter
Museum (for example, an eyedropper, liter pitcher, a measuring
cup with a scale in mL, and graduated cylinders of various sizes)
Student Page
so students can measure a wide range of capacities.
Date
Time
Discuss the goals for the collection, the kinds of objects to be
LESSON
Solving Capacity Problems
11 7
175
collected, and the procedures for adding objects to the museum.
Solve. You may draw pictures to help you.
1.
Adaline filled her watering can with 1,250 mL of water.
The procedure for adding items should probably be managed by
After watering her plants she had 485 mL left.
765
How much water did she use?
mL
students. Ask students to bring in objects for the museum over the
next week or two. This project will continue into the next unit. To
2.
Betty and Don spent the morning squeezing oranges
_
2
_
_
3
1
for juice. Betty squeezed 1
L and Don squeezed 1
L.
3
or 3.250
4
4
4
What is the total amount of juice?
L
ensure accuracy and to assess students’ skill in finding the capacity
of different objects, require that every item added to the museum
3.
There are 450 mL of syrup in 1 can. What is the
2,700
total amount of syrup in 6 cans?
mL
be measured by two or three students working independently.
_
2
This project will be revisited in Lesson 12-7.
4.
Dimitra poured
liter of water into a fish tank. William
5
_
4
poured
liter of water into the fish tank.
5
_
2
a.
5
How much more water did William pour?
L
400
b.
SMALL-GROUP
How many milliliters is that?
mL
Comparing Capacity Using
ACTIVITY
Metric Measures
5.
Raina brought a 1,500 mL jug of water to the school
picnic. Her water jug has enough water to fill 5 glasses.
300
mL
How much does each glass hold?
(Math Journal 2, p. 305A)
6.
The teacher set out 24 bowls of glue for the students
to use for an art project. Each bowl holds 75 mL of glue.
1,800
How much glue did the teacher need to fill all the bowls?
mL
Have students compare the capacity of 5 different size containers.
Ask students to predict which containers have the largest and
Math Journal 2, p. 305B
305A-305B_EMCS_S_MJ2_G4_U11_576426.indd 305B
3/16/11 11:14 AM
886
Unit 11 3-D Shapes, Weight, Volume, and Capacity
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6