Introductory Physics Worksheet With Answers - Mcas Review Packet #1 - Nnhs
ADVERTISEMENT
KEY
NNHS Introductory Physics: MCAS Review
Packet #1
Introductory Physics, High School
Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course
I . C
S
O N T E N T
T A N D A R D S
1. Motion and Forces
Central Concept: Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of
most objects.
1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (e.g., displacement, velocity, acceleration force,
linear momentum) and scalar quantities (e.g., distance, speed, energy, mass, work).
1.2 Distinguish between displacement, distance, velocity, speed, and acceleration. Solve
problems involving displacement, distance, velocity, speed, and constant acceleration.
1.3 Create and interpret graphs of 1-dimensional motion, such as position vs. time, distance
vs. time, speed vs. time, velocity vs. time, and acceleration vs. time where acceleration
is constant.
1.4 Interpret and apply Newton’s three laws of motion.
1.5 Use a free-body force diagram to show forces acting on a system consisting of a pair of
interacting objects. For a diagram with only co-linear forces, determine the net force
acting on a system and between the objects.
1.6 Distinguish qualitatively between static and kinetic friction, and describe their effects on
the motion of objects.
1.7 Describe Newton’s law of universal gravitation in terms of the attraction between two
objects, their masses, and the distance between them.
1.8 Describe conceptually the forces involved in circular motion.
2. Conservation of Energy and Momentum
Central Concept: The laws of conservation of energy and momentum provide alternate
approaches to predict and describe the movement of objects.
2.1 Interpret and provide examples that illustrate the law of conservation of energy.
2.2 Interpret and provide examples of how energy can be converted from gravitational
potential energy to kinetic energy and vice versa.
2.3 Describe both qualitatively and quantitatively how work can be expressed as a change in
mechanical energy.
2.4 Describe both qualitatively and quantitatively the concept of power as work done per unit
time.
2.5 Provide and interpret examples showing that linear momentum is the product of mass and
velocity, and is always conserved (law of conservation of momentum). Calculate the
momentum of an object.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11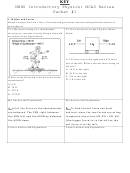 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24