Module-1 Algebra Quadratic Equations Worksheet With Answers Page 11
ADVERTISEMENT
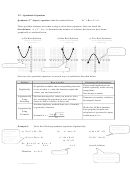
MODULE -
1
Quadratic Equations
Algebra
2
or
x
– 12x + 27 = 0
or
(x – 3) (x – 9) = 0
It gives x = 3 or x = 9
Notes
When first number x is 3, other number is 12 – 3 = 9 and when first number x is 9, other
number is 12 – 9 = 3.
Therefore, the required numbers are 3 and 9.
CHECK YOUR PROGRESS 6.5
1. The sum of the squares of two consecutive even natural numbers is 164. Find the
numbers.
2. The length of a rectangular garden is 7 m more than its breadth. If area of the garden
2
is 144 m
, find the length and breadth of the garden.
3. The sum of digits of a two digit number is 13. If sum of their squares is 89, find the
number.
4. The digit at ten's place of a two digit number is 2 more than twice the digit at unit's
place. If product of digits is 24, find the two digit number.
3
5. The sum of two numbers is 15. If sum of their reciprocals is
, find the two numbers.
10
LET US SUM UP
•
+ bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 and a, b, c are real numbers is called
2
An equation of the form ax
a quadratic equation in standard form.
•
The value(s) of the variable which satisfy a quadratic equation are called it roots or
solutions.
•
The zeros of a quadratic polynomial are the roots or solutions of the corresponding
quadratic equation.
•
+ bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0, into product of linear factors, then the
2
If you can factorise ax
2
roots of the quadratic equation ax
+ bx + c = 0, can be obtained by equating each
factor to zero.
•
+ bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 are given by
2
Roots of the quadratic equation ax
−
±
−
2
b
b
4
ac
2a
180
Mathematics Secondary Course
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14