Module-1 Algebra Quadratic Equations Worksheet With Answers Page 12
ADVERTISEMENT
MODULE -
1
Quadratic Equations
Algebra
•
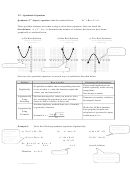
+ bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 It is
2
2
b
– 4ac is called discriminant of the quadratic equation. ax
usually denoted by D.
(i) If D > 0, then the quadratic equation has two real unequal (distinct) roots.
Notes
(ii) If D = 0, then the quadratic equation has two equal (coincident) roots.
(iii) If D < 0, then the quadratic equation has no real root.
TERMINAL EXERCISE
1. Which of the following are quadratic equations?
(
)
−
=
−
+
=
(i)
(ii)
2
y
y 5
3
0
5x
3
x
8
0
1
−
=
3x
5
2
(iii)
(iv) x(2x + 5) = x
+ 5x + 7
x
2. Solve the following equations by factorisation method:
2
(i) (x – 8) (x + 4) = 13
(ii) 3y
– 7y = 0
2
2
(iii) x
+ 3x – 18 = 0
(iv) 6x
+ x – 15 = 0
2
3. Find the value of m for which 5x
– 3x + m = 0 has equal roots.
2
4. Find the value of m for which x
– mx – 1 = 0 has equal roots.
5. Solve the following quadratic equations using quadratic formula:
2
2
(i) 6x
– 19x + 15 =0
(ii) x
+ x – 1 = 0
2
2
(iii) 21 + x = 2x
(iv) 2x
– x – 6 = 0
6. The sides of a right angled triangle are x – 1, x and x + 1. Find the value of x and hence
the sides of the triangle.
7. the sum of squares of two consecutive odd integers is 290. Find the integers.
8. The hypotenuse of a right angled triangle is 13 cm. If the difference of remaining two
sides is 7 cm, find the remaining two sides.
2
9. The sum of the areas of two squares is 41 cm
. If the sum of their perimeters is 36 cm,
find the sides of the two squares.
10. A right angled isosceles triangle is inscribed in a circle of radius 5 cm. Find the sides of
the triangle.
Mathematics Secondary Course
181
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14