Relating The Standard And Factored Forms Worksheet - Chapter 3.2 Page 6
ADVERTISEMENT
3.2
0 5 25t(t 2 4)
When the football hits the ground,
b)
the height is zero. h(t) 5 0 when
25t 5 0
t 2 4 5 0
and
each factor is 0. The zeros are
0 and 4. The football is on the
t 5 0
t 5 4
and
ground to start and then returns
4 s later.
t 5 0
t 5 4
c)
and
are the zeros.
I know that the maximum value is
0 1 4
the y-coordinate of the vertex, and it
t 5
lies on the axis of symmetry, which
2
is halfway between the zeros. The
t 5 2
is 25, which means
2
coefficient of
x
that the parabola opens down.
The ball reaches its maximum height
t 5 2
Therefore, there is a maximum
when
s.
t 5 2
value. The equation
is the axis
of symmetry.
I know the ball reaches the
h(t) 5 25t
1 20t
2
d)
maximum height at 2 s. So
h(2) 5 25(2)
1 20(2)
2
I calculated h(2), the maximum
5 220 1 40
height.
5 20
The maximum height is 20 m.
h(t)
e)
25
I marked the two zeros and the
vertex that I found on graph paper.
20
Since a < 0, those three points are
15
part of a parabola that opens
down, so I joined them by
10
sketching a parabola. I can see
5
from the graph that the y-intercept
t
is 0. This is also seen in the function
0
1
1
2
3
4
5
when it’s written in standard form:
h(t) 5 25t
1 20t 1 0
2
.
Time (s)
If you are given the graph of a quadratic function and you can determine the zeros
and the coordinates of another point on the parabola, you can determine the
equation of the function in factored and standard forms.
137
Working with Quadratic Functions: Standard and Factored Forms
NEL
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5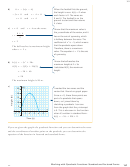 6
6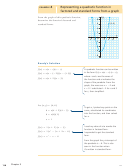 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11








