Relating The Standard And Factored Forms Worksheet - Chapter 3.2 Page 9
ADVERTISEMENT
PRACTISING
For each quadratic function, determine the zeros, the equation of the
4.
axis of symmetry, and the coordinates of the vertex without graphing.
g(x) 5 2x(x 1 6)
g(x) 5 (2x 1 5) (9 2 2x)
a)
d)
g(x) 5 (x 2 8) (x 1 4)
g(x) 5 (2x 1 3) (x 2 2)
b)
e)
g(x) 5 (x 2 10) (2 2 x)
g(x) 5 (5 2 x) (5 1 x)
c)
f )
Express each function in factored form. Then determine the zeros, the
5.
equation of the axis of symmetry, and the coordinates of the vertex
without graphing.
g(x) 5 3x
2 6x
g(x) 5 3x
1 12x 2 15
2
2
a)
d)
g(x) 5 x
1 10x 1 21
g(x) 5 2x
2 13x 2 7
2
2
b)
e)
g(x) 5 x
2 x 2 6
g(x) 5 26x
1 24
2
2
c)
f )
Match the factored form on the left with the correct standard form on
6.
the right. How did you decide on your answer?
y 5 (2x 1 3) (x 2 4)
y 5 4x
2 19x 1 12
2
a)
i)
y 5 (4 2 3x) (x 1 3)
y 5 23x
2 5x 1 12
2
b)
ii)
y 5 (3x 2 4) (x 2 3)
y 5 2x
2 5x 2 12
2
c)
iii)
y 5 (3 2 4x) (4 2 x)
y 5 3x
2 13x 1 12
2
d)
iv)
y 5 (x 1 3) (3x 2 4)
y 5 3x
1 5x 2 12
2
e)
v)
Determine the maximum or minimum value for each quadratic
7.
function.
f (x) 5 (7 2 x) (x 1 2)
g(x) 5 x
1 7x 1 10
2
a)
d)
f (x) 5 (x 1 5) (x 2 9)
g(x) 5 2x
1 25
2
b)
e)
f (x) 5 (2x 1 3) (8 2 x)
g(x) 5 4x
1 4x 2 3
2
c)
f )
Graph each quadratic function by hand by determining the zeros,
8.
K
vertex, axis of symmetry, and y-intercept.
g(x) 5 (2x 2 1) (x 2 4)
g(x) 5 2x
1 2x 2 12
2
a)
d)
f (x) 5 (3x 2 1) (2x 2 5)
f (x) 5 2x
2 2x 1 24
2
b)
e)
f (x) 5 x
2 x 2 20
f (x) 5 24x
2 16x 1 33
2
2
c)
f )
When a quadratic function is in standard form, what information
9. a)
about the graph can be easily determined? Provide an example.
When a quadratic function is in factored form, what information
b)
about the graph can be easily determined? Provide an example.
140
Chapter 3
NEL
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5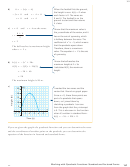 6
6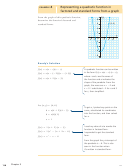 7
7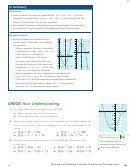 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11








