Chapter 11 Probability Worksheet Page 20
ADVERTISEMENT
286
PROBABILITY (Chapter 11)
When considering a situation like this:
²
if two events have no common outcomes we say they are
mutually
or
exclusive
disjoint
²
if two events have common outcomes they are
.
not mutually exclusive
suit
S
H
D
C
value
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
J
Q
K
A
8
4
4
8
Notice that: P(ace or seven) =
and P(ace) + P(seven) =
+
=
52
52
52
52
So,
if two events A and B are mutually exclusive then
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B)
suit
S
H
D
C
value
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
J
Q
K
A
16
13
4
17
Notice that: P(heart or seven) =
and P(heart) + P(seven) =
+
=
:
52
52
52
52
Actually, P(heart or seven) = P(heart) + P(seven) ¡ P(heart and seven).
So,
if two events A and B are not mutually exclusive then
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) ¡ P(A and B).
EXERCISE 11H
An ordinary die with faces 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 is rolled once. Consider these events:
1
getting a 1
getting a 3
A:
B:
C:
getting an odd number
D:
getting an even number
getting a result greater than 3.
E:
getting a prime number
F :
a
List all possible pairs of events which are mutually exclusive.
b
Find:
i
P(B or D)
ii
P(D or E)
iii
P(A or E)
iv
P(B or E)
v
P(C or D)
vi
P(A or B or F ).
2
A coin and an ordinary die are tossed simultaneously.
Draw a grid showing the 12 possible outcomes.
a
a head and a 5
a head or a 5:
b
Find the probabilites of getting:
i
ii
P(H or 5) = P(H) + P(5) ¡ P(H and 5).
c
Check that:
3
Two ordinary dice are rolled.
Draw a grid showing the 36 possible outcomes.
a
a 3 and a 4
a 3 or a 4:
b
Find the probability of getting:
i
ii
P(3 or 4) = P(3) + P(4) ¡ P(3 and 4).
c
Check that:
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4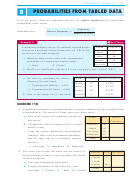 5
5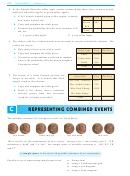 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14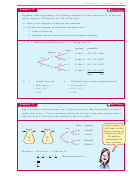 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21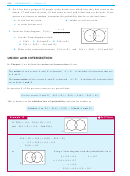 22
22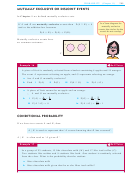 23
23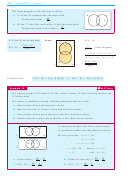 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28








