Electronegativity And Bonding Worksheet
ADVERTISEMENT
Electronegativity and Bonding
Model 1: Electronegativitiy
When two bonded atoms are the same (e.g. C-C, O-O, H-H etc), the bonding electrons are shared equally. When
the two atoms are different, one of the atoms attracts the bonding electrons more strongly. The ability of an
atom to attract the electrons in a bond is called the electronegativity. It is possible to quantify this on a scale.
H
2.30
Li
Be
B
C
N
O
F
0.91
1.58
2.05
2.54
3.07
3.61
4.19
Na
Mg
Al
Si
P
S
Cl
0.87
1.29
1.61
1.92
2.25
2.59
2.87
K
Ca
Ga
Ge
As
Se
Br
0.73
1.03
1.76
1.99
2.21
2.42
2.69
Rb
Sr
In
Sn
Sb
Te
I
0.71
0.96
1.66
1.82
1.98
2.16
2.36
Critical thinking questions
1.
Describe the trend in electronegativity as one moves from left to right across a period.
2.
Describe the trend in electronegativity as one moves down a group.
3.
Compare the trends in questions 2 and 3 to the corresponding trends in ionization energy and explain
any relationship you observe.
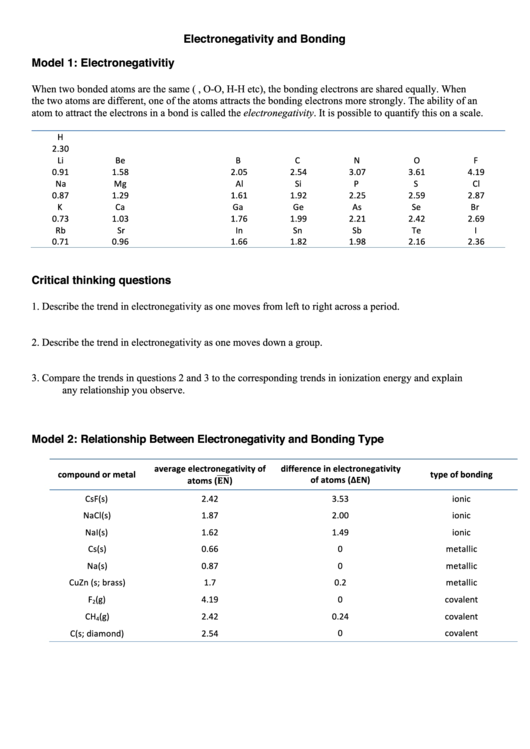
Model 2: Relationship Between Electronegativity and Bonding Type
average
e lectronegativity
o f
difference
i n
e lectronegativity
compound
o r
m etal
type
o f
b onding
atoms
( ����)
of
a toms
( ΔEN)
CsF(s)
2.42
3.53
ionic
NaCl(s)
1.87
2.00
ionic
NaI(s)
1.62
1.49
ionic
Cs(s)
0.66
0
metallic
Na(s)
0.87
0
metallic
CuZn
( s;
b rass)
1.7
0.2
metallic
F
(g)
4.19
0
covalent
2
CH
(g)
2.42
0.24
covalent
4
C(s;
d iamond)
2.54
0
covalent
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2