Uv-Visible Spectroscopy - Spectra Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s
3. Beta-carotene has the following structure. The red parts are all conjugated double bonds.
Beta-carotene absorbs strongly throughout the UV, and has strong absorptions in the visible region
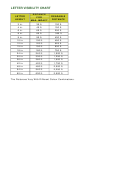
between 400 and 500 nm, peaking at about 470 nm. Use this table to explain why beta-carotene is
orange.
4. a) Phenolphthalein exists in two forms depending on the pH of the solution:
Redraw these structures showing the extent of the delocalisation in each one in red.
b) Use your diagrams to explain why adding the alkali shifts the colour from colourless to magenta.
c) Methyl orange exists in two forms, one yellow (with a maximum peak in its spectrum at about
440 nm) and the other red (with maximum peak at about 520 nm).
(i) Explain briefly why the two forms are the colours they are.
(ii) Which of these forms has the greater amount of delocalisation?
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3