Acids & Bases Calculations Student Notes Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
Ionization Constant of Water (K
)
V.
w
A. When water ionizes itself it produces both hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions
↔
+
–
H
O (l )
H
(aq) + OH
(aq)
2
B. Water has equal concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxide ions
C. [H
+
] of water is 1.0 × 10
–7
M
D. [OH
–
] of water is 1.0 × 10
–7
M
–14
2
E. K
= 1.00 × 10
(mol/L)
w
+
–
F. FORMULA: K
= [H
] x [OH
]
w
–
+
–7
G. Example #5: What is the [OH
] for a solution with a [H
] of 9.6 x 10
M?
H. Example #6: Determine the pH of a solution with [OH
–
] = 3.6 x 10
–9
. (Hint: Perform 2
calculations!)
pOH Calculations
VI.
A. pOH – logarithmic scale which expresses base and acid strengths relative to their hydroxide
ion concentrations.
B. pOH is calculated using the equation
C. Concentration in units of molarity
D. Example #7: What is the pOH of a solution in which the hydroxide ion concentration is 1.0 ×
10
–9
M?
E. Example #8: Determine the pOH of a 0.0034 M HNO
solution.
3
–
[OH
] Calculations
VII.
–
–
–pOH
A. OH
] is calculated using the equation: [OH
] = 10
B. Example #9: Calculate the [OH
–
] for a solution with a pOH of 8.7.
–
C. Example #10: Calculate the [OH
] for a solution with a pOH of 6.2.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3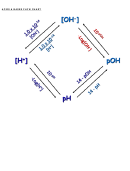 4
4








