Using A Scientific Approach
ADVERTISEMENT
1.2 Using a Scientific Approach (Scientific Method) - NOTES
Put the bold terms below into the numbered spaces of the flow chart on the other side of this paper.
1. Make observations: information ________________ by using your _______________ senses. Hearing,
____________, smelling, touching, or _____________. We don’t often taste in science. EXAMPLE – I see
that my flashlight is not working.
2. Ask a question: _____________ previous knowledge and what you want to find out about your
observations you can develop a question you’ll answer. EXAMPLE – Is it the batteries? ____________
3. Develop a hypothesis a _______________ and ________________ explanation for why something is -
____________________. Will usually _______________ what you would like the ________________ to be. We
will practice developing “________ … __________ …” statements. EXAMPLE – If I change the batteries
then the flashlight will work.
4. Test hypothesis with a controlled experiment – an experiment where only one _______________ is
changed at a time. All ___________ variables are ______________ or kept constant. A ___________ that
can _______________ in an experiment is called a variable.
a. manipulated/independent variable – what the scientist ________________, it will cause a
change in the responding variable. EXAMPLE batteries
b. responding/dependent variable – the _________________, what is __________________ in the
end, this variable changes in ________________ to the manipulated variable. EXAMPLE
flashlight working
5. Collect, analyze, and evaluate data – gather ____________, see what ___________ is telling you.
a. qualitative data –_____________ or descriptions, written ___________. EXAMPLE The light is
bright.
b. quantitative data – ____________ and measurements. EXAMPLE – The light blinked 3 times.
6. Draw a conclusion - based on your_________ you can make a ____________ about your results; you
____________ include data that supports your statement.
a. Hypothesis is supported – your data ___________ your hypothesis; ____________ tests to get
more evidence/support. EXAMPLE The light shines after I changed the batteries.
b. Hypothesis is rejected – your data ________________ support your hypothesis, revise your
_____________, hypothesis, and _____________ steps 4 -5. EXAMPLE The flashlight doesn’t
work after the batteries were changed. *** Develop _______ question: Is it the bulb?
***Develop ________ hypothesis: If I change the bulb, then the flashlight will work. ***Retest
with _______ experiment.
7. Develop Theory: a ________________ explanation for observations and __________ collected from
________ experiments. ___________ if your hypothesis is supported by _________________ tests and
_________ of evidence can a ___________ be made.
1
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1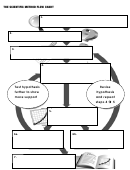 2
2








