Revision Guide Alkenes 3.4 - Chemistry Sheet Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
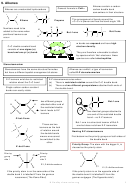
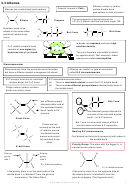
3. Reaction of Sulphuric acid with Alkenes
Stage 1
Stage 2
Change in functional group
Change in functional group
alkene
alkyl hydrogensulphate
alkyl hydrogensulphate
alcohol
Reagents: concentrated H
SO
Reagents: water
2
4
Conditions: room temperature
Conditions: warm mixture
Mechanism: Electrophilic Addition
Type of reaction: hydrolysis
Type of reagent: Electrophile, H
SO
2
4
CH
CH
OSO
OH + H
O
CH
CH
OH + H
SO
3
2
2
2
3
2
2
4
CH
=CH
+ H
SO
CH
CH
OSO
OH
2
2
2
4
3
2
2
Stage 1: electrophilic addition
H
SO
is best
2
4
drawn as
H
H
H
H
H
H
H-OSO
OH
+
2
H
C
C
C
H
H
C
C
C
H
H
C
C
C
H
3
3
3
in exams. Its real
+
H
δ
H
H
structure is
OSO
OH
2
-
:OSO
OH
O
OSO
OH
2
H
O
2
-
δ
S
Stage 2: hydrolysis
O
H
O
H
H
H
+ H
O
+ H
SO
Overall role of
H
C
C
CH
H
C
C
C
H
2
2
4
3
3
3
sulphuric acid is that
H
OH
of a catalyst (as it is
OSO
OH
2
regenerated)
With unsymmetrical alkenes a minor and major product can also be formed similar to the
addition of HBr. The same explanation applies.
Definition: Hydrolysis – a reaction where the molecule is split by the addition of water
Direct Industrial hydration of alkenes to form alcohols
This reaction can be called
hydration: a reaction where
Industrially alkenes are converted to alcohols in one step rather than the
water is added to a molecule
two in the above sulphuric acid reaction. They are reacted with water in
the presence of an acid catalyst.
Essential Conditions
High temperature 300 to 600°C
=
CH
CH
+ H
O
CH
CH
OH
2
2 (g)
2
(g)
3
2
(l)
High pressure 70 atm
Catalyst of concentrated H
PO
3
4
The high pressures needed mean this cannot be done in the laboratory. It is preferred industrially, however,
as there are no waste products and so has a high atom economy. It would also mean separation of products
is easier (and cheaper) to carry out. See equilibrium chapter for more on the industrial conditions for this
reaction.
Testing for Alkenes with Bromine water
Bromine water decolourises in the presence of a double bond. This can be used as a
test for the presence of an double bond in a molecule. It can be used quantitatively to
show the presence of multiple double bonds in compounds like polyunsaturated oils.
N Goalby
3
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1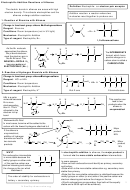 2
2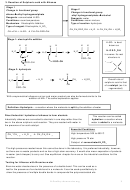 3
3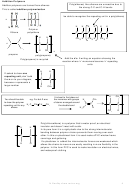 4
4