Dizziness In Orthopaedic Physical Therapy Practice: History And Physical Examination Page 22
ADVERTISEMENT
that does not allow for compensation by the cervico-
reported on the possible prognostic value of a reversal of
ocular reflex (COR).
nystagmus direction towards the affected ear to predict
an imminent recurrence of Meniere’s disease.
Dynamic Visual Acuity
Head Thrust Test
After establishing baseline visual acuity with a Snel-
len chart, this test measures visual acuity with concur-
The head thrust test (Figures 6A & B) may also de-
rent head movement. The head is moved from side to
tect an impaired VOR
. The patient fixates gaze on the
112
side at a frequency of 1 Hz while the patient reads the
therapist’s nose. The therapist then moves the patient’s
Snellen chart
. A decrease by two lines is suspicious and
head in the horizontal plane in a rapid, passive manner
41
by three or more is indicative of an abnormal VOR
.
with unpredictable timing and direction (5-10
at 3000-
41,94
0
This test is not suited for detecting unilateral peripheral
4000
s
). A patient with vestibular loss will have difficulty
0
-1
or central vestibular lesions but is indicated in case of
maintaining gaze fixation, requiring a corrective saccade
suspected bilateral vestibular loss
. Herdmann, Blatt,
(fast eye movement) to maintain gaze fixation on the
41,109
and Schubert
reported poor reliability for this test.
nose
. A corrective saccade following head thrust right
4
75
indicates the vestibular loss is on the right; corrective
Doll’s Head Test
saccades with head thrust left suggest an involved left
The examiner faces the patient, who fixes gaze on
side
. Schubert et al
reported a sensitivity of 71%
113
114
the examiner’s nose. The examiner then oscillates the
and a specificity of 82% for the head thrust test with the
patient’s head 30
side to side at 0.5-1 Hz. Eye move-
head tilted down 30
in the diagnosis of patients with
0
0
ments that are not smooth but interrupted by catch-up
unilateral vestibular loss and 84% sensitivity and 82%
saccades towards the fixation target indicate bilateral
specificity for bilateral loss.
vestibular lesions
. We found no data on reliability
41
and validity.
BPPV Tests
Head-Shaking Nystagmus Test
These tests look for canalithiasis or cupulolithiasis
The examiner vigorously moves the patient’s head
in all SCC. A positive response on these tests in combi-
back and forth horizontally for about 30 seconds with
nation with corroborating history findings and in the
the patient’s eyes closed. Upon opening the eyes, the
absence of findings indicative of other pathology implies
nystagmus will beat away from the side of a unilateral
that sole PT management may be indicated.
peripheral vestibular lesion
or towards the lesioned
109
Hallpike-Dix Maneuver
side in patients with Meniere’s disease
. When compared
110
to a caloric test, the head-shaking nystagmus test (with
This maneuver (Figures 7A & B) tests all SSC
.
41
Frenzel glasses) had 66% sensitivity and 77% specificity
The long sitting patient turns the head 45
and is then
0
for detecting canal paresis >20%
. Kamei and Iizuka
assisted to supine with the rotated head 30
below
111
110
0
Fig. 5:
Fig. 5:
F
Hautant test
Dizziness in Orthopaedic Physical Therapy Practice:
History and Physical Examination / 243
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Medical
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21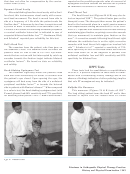 22
22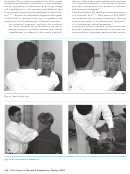 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30








