Dizziness In Orthopaedic Physical Therapy Practice: History And Physical Examination Page 23
ADVERTISEMENT
horizontal. This position is maintained for ≥30 seconds.
thiasis)--deflects the cupula and alters the posterior
Delayed-onset, torsional, horizontal, or (less commonly)
SCC neuronal firing rate
. This results in an apo-
115
vertical nystagmus in combination with vertigo lasting
geotropic (beating away from the earth or downside
<60 (canalithiasis) or >60 seconds (cupulolithiasis) that
ear) torsional nystagmus
.
115
decreases with repeated testing constitutes a positive find-
A bilateral positive test implicates either the anterior
•
ing
. Relevant for differential diagnosis with regards
or horizontal SCC
. With anterior SCC BPPV,
41,76,115
41,76
to which SSC is involved is the type of nystagmus and
the ipsilateral test provokes a geotropic (beating
whether the test is unilaterally or bilaterally positive:
towards the earth or the affected ear) torsional
115
An ipsilateral maneuver positions the posterior
or a downbeating vertical nystagmus
.
76
•
SCC of the downside ear in the plane of the pull of
A bilaterally positive test with a purely horizontal
•
gravity. Shifting of otoconia--whether free-floating
geotropic (beating in the direction of the face turn
(canalithiasis) or adhered to the cupula (cupuloli-
or downside ear) nystagmus implicates the horizon-
Fig. 6:
Fig. 6:
F
Head thrust test
A.
B.
Fig. 7a-b:
Fig. 7a-b:
F
Hallpike-Dix maneuver
244 / The Journal of Manual & Manipulative Therapy, 2005
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Medical
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21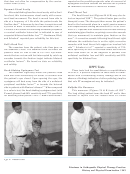 22
22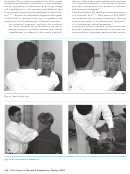 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30








